- Home
- Articles
- Architectural Portfolio
- Architectral Presentation
- Inspirational Stories
- Architecture News
- Visualization
- BIM Industry
- Facade Design
- Parametric Design
- Career
- Landscape Architecture
- Construction
- Artificial Intelligence
- Sketching
- Design Softwares
- Diagrams
- Writing
- Architectural Tips
- Sustainability
- Courses
- Concept
- Technology
- History & Heritage
- Future of Architecture
- Guides & How-To
- Art & Culture
- Projects
- Interior Design
- Competitions
- Jobs
- Store
- Tools
- More
- Home
- Articles
- Architectural Portfolio
- Architectral Presentation
- Inspirational Stories
- Architecture News
- Visualization
- BIM Industry
- Facade Design
- Parametric Design
- Career
- Landscape Architecture
- Construction
- Artificial Intelligence
- Sketching
- Design Softwares
- Diagrams
- Writing
- Architectural Tips
- Sustainability
- Courses
- Concept
- Technology
- History & Heritage
- Future of Architecture
- Guides & How-To
- Art & Culture
- Projects
- Interior Design
- Competitions
- Jobs
- Store
- Tools
- More
Exploring American Architecture: A Journey Through Styles and Cultural Influences
Dive into the fascinating world of American architecture in this article that traces its vibrant history and diverse styles. From Colonial symmetry to modern minimalism, discover how cultural influences and historical events shape the designs of homes and skyscrapers alike.
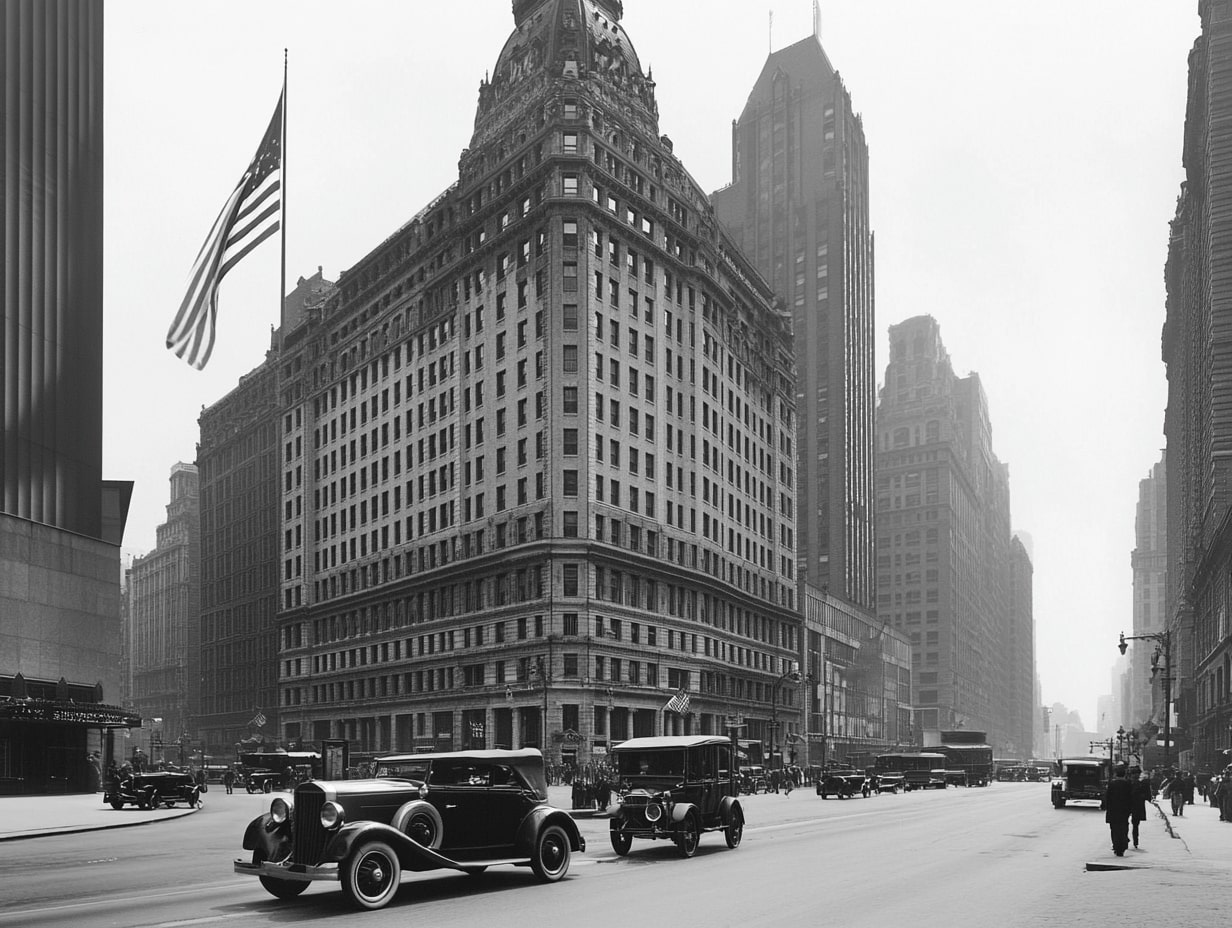

Table of Contents Show
American architecture tells a captivating story of innovation and diversity. From the colonial homes of New England to the sleek skyscrapers of modern cities, each structure reflects the unique cultural influences and historical events that shaped our nation. As we explore this rich tapestry, we’ll uncover how different styles emerged, evolved, and continue to influence the way we build today.
Throughout the centuries, architects have pushed boundaries, blending functionality with artistry. Whether it’s the grandeur of Neoclassical buildings or the boldness of contemporary designs, American architecture showcases our values, aspirations, and creativity. Join us as we delve into the fascinating world of architectural styles that define our landscapes and inspire future generations.

Introduction to American Architecture
American architecture features a dynamic blend of styles reflecting the nation’s diverse cultural influences. We observe roots in Colonial, Native American, and European traditions, all converging to create a unique architectural landscape.

Key periods in American architecture include:
- Colonial: Characterized by symmetrical designs and functional layouts, Colonial architecture showcases timber framing and simple forms. Notable examples include early Georgian and Federal homes, emphasizing order and harmony.
- Gothic Revival: Popular in the mid-19th century, this style reflects medieval European elements. Features include pointed arches, intricate ornamentation, and decorative stonework, evident in structures like churches and universities.
- Victorian: The Victorian era introduced elaborate details, asymmetrical shapes, and vibrant colors. Styles such as Queen Anne and Romanesque Revival emphasized artistic expression through materials and design.
- Modernism: Emerging in the early 20th century, modernism marked a move towards minimalism. Innovations in materials like steel and glass improved functionality, creating iconic buildings such as the Guggenheim Museum by Frank Lloyd Wright and the Seagram Building by Mies van der Rohe.
- Postmodernism: Rising in the late 20th century, postmodern architecture reacted against strict modernist principles. It embraced eclectic styles, playful forms, and historical references, demonstrated in works like the Portland Building by Michael Graves.
American architecture continuously evolves, shaped by technological advancements and cultural dialogues. We celebrate its ability to narrate stories and foster identities, often reflecting our societal values and aspirations through time.
Historical Development
American architecture showcases a rich historical trajectory shaped by cultural and societal influences. Key architectural styles reflect the evolution of design philosophies and materials throughout different periods.

Colonial Architecture
Colonial architecture emerged in the 17th and 18th centuries, influenced by European settlers. This style features symmetrical designs, gabled roofs, and central doorways. Common materials included wood and brick, aligning with regional availability. Notable examples are the Georgian-style homes in New England, recognized for their proportionate and structured appearance. These houses emphasized functional layouts, often with large central hearths, meeting the needs of early American families.
19th Century Innovations
The 19th century brought significant innovations in American architecture due to industrial advancements and expanding urbanization. The introduction of iron and steel transformed building capabilities, allowing for taller structures and greater design freedom. Architectural movements like Gothic Revival and Victorian architecture emerged during this period, characterized by ornate details, intricate facades, and vibrant color palettes. Key examples include San Francisco’s Painted Ladies and the Gothic cathedrals in major cities, which displayed the period’s craftsmanship and aesthetic diversity. This century laid the groundwork for modern architectural experimentation, blending artistic expression with function.
Key Architectural Styles
American architecture features a variety of styles that reflect the nation’s cultural heritage and historical evolution. We explore some of the most significant architectural movements that have shaped our built environment.

Federal Style
Federal Style emerged in the late 18th to early 19th centuries, characterized by its emphasis on symmetry and classicism. Buildings in this style often showcase flat roofs, elegant columns, and decorative pediments. They frequently include features such as a central entrance, large windows, and brick or wood facades painted in muted colors. Notable examples include the Massachusetts State House and the Baltimore Museum of Art.
Gothic Revival
Gothic Revival gained popularity in the 19th century, drawing inspiration from medieval European architecture. This style is known for its pointed arches, intricate detailing, and decorative elements like tracery and spires. Often used for churches and civic buildings, Gothic Revival captures a sense of grandeur and spirituality. Prominent examples include the Cathedral of Saint John the Divine in New York City and the Smithsonian Castle in Washington, D.C.
Modernism
Modernism rose to prominence in the early to mid-20th century, focusing on simplicity and functionality. This architectural movement embraces clean lines, open spaces, and the use of new materials like steel and glass. Modernist buildings often have minimal ornamentation, emphasizing form over decoration. Iconic examples include the Glass House by Philip Johnson and the Seagram Building by Mies van der Rohe, both of which illustrate the principles of modernist design while creating inspirational spaces.
Contemporary Trends
Contemporary American architecture reflects a fusion of sustainability, technology, and innovative design. We observe several key trends shaping the landscape today.

- Sustainable Design
Sustainability becomes a priority with eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient practices. Architectures achieve LEED certification by using reclaimed materials, integrating solar panels, and implementing green roofs. Notable examples include the Bullitt Center in Seattle, recognized for its net-zero energy consumption.
- Smart Technology Integration
Smart home technologies enhance convenience and efficiency. Architects incorporate automation, energy monitoring systems, and smart appliances into designs, leading to improved living experiences. These innovations attract consumers interested in cutting-edge homes.
- Open Space Concepts
Open floor plans gain popularity, fostering connectivity within residential and commercial spaces. We design versatile spaces that allow for fluid movement and adaptability, accommodating both work and leisure. This concept brings a sense of community into modern living.
- Adaptive Reuse
Adaptive reuse of existing buildings preserves historical character while meeting current needs. Renovation of warehouses into loft apartments or repurposing industrial sites captures unique aesthetics and fosters a sense of place. Cities like Philadelphia showcase success stories of this trend.
- Minimalism and Maximalism
Minimalism emphasizes simplicity through clean lines and functional designs. Conversely, maximalism embraces vibrant colors and bold patterns, celebrating individuality. Architects increasingly experiment with blending these styles, creating dynamic environments that reflect diverse preferences.
- Culturally Responsive Design
Culturally responsive architecture incorporates local traditions and materials. We see designs that honor regional heritage while promoting inclusivity. The National Museum of African American History and Culture in Washington, D.C., exemplifies this unique fusion.
- Biophilic Design
Biophilic design prioritizes natural elements, integrating greenery and natural light within structures. Architects create environments that enhance mental well-being and productivity by fostering a connection with nature. This trend thrives in urban settings, transforming indoor spaces into serene retreats.
- High-Performance Materials
Advances in materials technology lead to stronger, lighter, and more durable options. Architects utilize materials like cross-laminated timber and transparent aluminum to create innovative structures that prioritize both aesthetics and performance.
These contemporary trends not only push the boundaries of American architecture but also redefine the way we interact with our built environments. They echo our collective values and adapt to the changing needs of society.
Conclusion
American architecture showcases a rich tapestry of styles and influences that reflect our diverse history and cultural evolution. Each architectural period encapsulates a unique philosophy and artistic expression, contributing to the character of our urban and rural landscapes.
Highlighting Colonial architecture, we see how symmetrical designs and practical layouts serve as a foundation for American residential spaces. The emergence of Gothic Revival and Victorian architecture during the 19th century illustrates the impact of industrial advancements and a growing appetite for ornate aesthetics. Structures like San Francisco’s Painted Ladies and impressive cathedrals remind us of this creative explosion.
We observe the transition into Modernism that prioritizes simplicity and functionality, redefining our approach to space with iconic buildings such as the Glass House and the Seagram Building. This shift set the stage for contemporary architecture that embraces sustainability, advanced technology, and innovative designs.
In our present landscape, we witness trends that emphasize eco-friendly materials along with smart technology integration. The adaptive reuse of buildings showcases our commitment to preserving historical elements while catering to modern needs. We acknowledge culturally responsive architecture, which respects local traditions, and biophilic design, which incorporates natural aspects to enhance well-being.
Ultimately, the evolution of American architecture is an ongoing narrative that continues to shape our identities and community values, inviting exploration and appreciation for the remarkable structures that define our environment.
- American architectural heritage
- American architecture exploration
- American architecture styles
- architectural evolution in USA
- architectural journey USA
- architecture cultural influences
- architecture history United States
- cultural architecture trends USA
- cultural impacts on US architecture
- exploring US architecture
- famous American architects
- historical architecture USA
- history of American architecture
- iconic American buildings
- modern American architecture
- popular US architectural styles
- style influences in architecture
- traditional American architecture
- US cultural architecture
I create and manage digital content for architecture-focused platforms, specializing in blog writing, short-form video editing, visual content production, and social media coordination. With a strong background in project and team management, I bring structure and creativity to every stage of content production. My skills in marketing, visual design, and strategic planning enable me to deliver impactful, brand-aligned results.
Submit your architectural projects
Follow these steps for submission your project. Submission FormLatest Posts
Shigeru Ban Architecture: Vision, Awards & Humanitarian Design
Discover how Shigeru Ban revolutionized architecture with paper tubes, disaster relief shelters,...
Revolutionizing Video Commerce: How E-Commerce Brands Are Scaling Product Videos with AI
Table of Contents Show The Product Video Problem: Why Scale MattersThe Seedance...
The Complete Beginner DIY Plumbing Checklist: A Step-by-Step Guide for First-Time Home Projects
Table of Contents Show Step 1: Confirm the Job Is Truly Beginner-FriendlyStep...
Top Job Alternatives for Architects and Interior Designers
Explore diverse job alternatives for architects and interior designers, from creative roles...











Leave a comment