- Home
- Articles
- Architectural Portfolio
- Architectral Presentation
- Inspirational Stories
- Architecture News
- Visualization
- BIM Industry
- Facade Design
- Parametric Design
- Career
- Landscape Architecture
- Construction
- Artificial Intelligence
- Sketching
- Design Softwares
- Diagrams
- Writing
- Architectural Tips
- Sustainability
- Courses
- Concept
- Technology
- History & Heritage
- Future of Architecture
- Guides & How-To
- Projects
- Interior Design
- Competitions
- Jobs
- Store
- Tools
- More
- Home
- Articles
- Architectural Portfolio
- Architectral Presentation
- Inspirational Stories
- Architecture News
- Visualization
- BIM Industry
- Facade Design
- Parametric Design
- Career
- Landscape Architecture
- Construction
- Artificial Intelligence
- Sketching
- Design Softwares
- Diagrams
- Writing
- Architectural Tips
- Sustainability
- Courses
- Concept
- Technology
- History & Heritage
- Future of Architecture
- Guides & How-To
- Projects
- Interior Design
- Competitions
- Jobs
- Store
- Tools
- More
The Intersection of Sustainability and Architecture
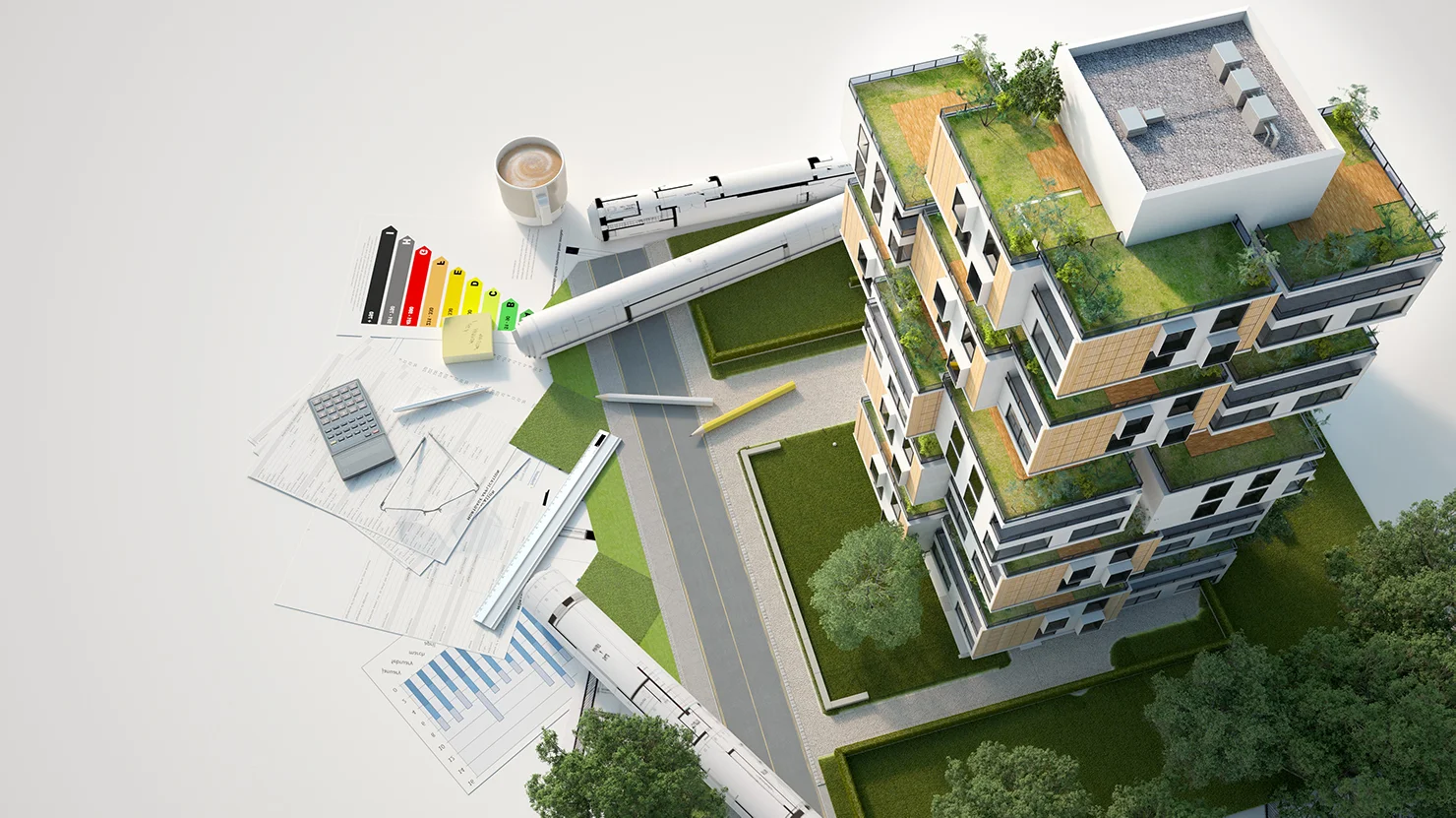

As we face the daunting challenge of climate change, architects around the world are rethinking the way they approach design. The intersection of sustainability and architecture has become a central focus for the industry, as professionals seek to create buildings that are not only aesthetically pleasing, but also environmentally responsible. In this essay, we will explore the importance of sustainability in architecture, the principles that guide sustainable design, and examples of sustainable buildings around the world.
Sustainability in architecture is essential because buildings are responsible for a significant portion of global greenhouse gas emissions. According to the United Nations Environment Programme, buildings account for nearly 40% of global CO2 emissions, as well as a substantial amount of energy consumption and waste production. To combat this, architects are using innovative approaches to reduce the environmental impact of buildings while also improving their functionality and livability.

Sustainability Principles
The principles that guide sustainable design are diverse and complex, but they all revolve around the idea of minimizing a building’s negative impact on the environment. This can be achieved through a variety of means, including:
- Energy Efficiency: Designing buildings that require less energy to heat, cool, and power.
- Sustainable Materials: Using environmentally responsible materials in construction, such as recycled materials or those sourced from renewable resources.
- Water Conservation: Designing buildings that use less water and incorporate water-efficient features such as rainwater harvesting systems.
- Passive Design: Utilizing natural light and ventilation to reduce the need for artificial lighting and air conditioning.
- Green Roofs and Walls: Incorporating vegetation into buildings to reduce heat absorption, provide insulation, and improve air quality.
- Adaptive Reuse: Repurposing existing buildings instead of demolishing and rebuilding, reducing waste and preserving historic architecture.
- Life Cycle Analysis: Assessing the environmental impact of a building from construction through its entire lifespan, including demolition and disposal.
These principles are not mutually exclusive and can be combined to create innovative solutions to complex problems. For example, designing a building with passive heating and cooling systems that utilize renewable energy sources, sustainable materials, and green roofs can significantly reduce a building’s carbon footprint.

Sustainable Buildings in Architecture
There are countless examples of sustainable buildings around the world that demonstrate the effectiveness of sustainable design principles. One such example is the Bullitt Center in Seattle, Washington. The Bullitt Center is a net-zero energy building, meaning it produces as much energy as it consumes. It achieves this through a combination of solar panels, geothermal heating and cooling systems, and passive design features such as a green roof and rainwater harvesting. The building also incorporates asustainable materials and is designed to be easily disassembled and recycled at the end of its life.
The intersection of sustainability and architecture is critical in building a greener future. Architects must consider the environmental impact of their designs and prioritize the principles of sustainability in their work. By utilizing innovative approaches such as energy efficiency, sustainable materials, and passive design, architects can create buildings that are not only environmentally responsible but also functional and livable. Sustainable buildings such as the Bullitt Center and the Edge demonstrate the effectiveness of these principles and provide a roadmap for a greener future.

Examples of Current Sustainable Buildings
There are many examples of sustainable buildings around the world that incorporate innovative approaches to reduce their environmental impact. Here are just a few current examples:
One Angel Square – Manchester, UK
This office building, completed in 2013, is considered one of the greenest in the world. It is designed to use 80% less energy than a typical office building, and incorporates features such as a biomass boiler, rainwater harvesting, and natural ventilation.

The Edge – Amsterdam, Netherlands
Completed in 2014, this office building has been dubbed the “smartest building in the world.” It utilizes an array of sensors and data analytics to optimize its energy use, adjust lighting and temperature based on occupancy and weather patterns, and provide personalized workspace preferences for employees. The building also incorporates sustainable materials and features a green wall with over 70,000 plants.

Bosco Verticale – Milan, Italy
Completed in 2014, this residential tower is designed to incorporate trees and plants on each floor. The building is intended to improve air quality, reduce energy consumption, and provide residents with access to green space.

The Crystal – London, UK
This sustainable building, completed in 2012, is designed to be a showcase for sustainable technologies. It incorporates features such as solar panels, ground source heat pumps, and rainwater harvesting, and is designed to use half the energy of a typical office building. The building also includes an exhibition space that showcases sustainable technologies and innovations.

Submit your architectural projects
Follow these steps for submission your project. Submission FormLatest Posts
The Vertical Revolution: How Basement Underpinning Creates Architectural Gold from Forgotten Spaces
Think about the last time you walked into a room with soaring...
Best Tools for Tracking Construction Labor Hours
Quick View of the Products Listed Best Overall: Workyard – Complete construction...
More Than a Gate: Designing a Secure and Stylish Home Entryway
A property’s entrance tells a story before a single guest steps inside....
Employer Liability and Smartphones: When Work Texts Cause Crashes
In today’s connected world, it’s nearly impossible to separate work from daily...











Leave a comment