- Home
- Articles
- Architectural Portfolio
- Architectral Presentation
- Inspirational Stories
- Architecture News
- Visualization
- BIM Industry
- Facade Design
- Parametric Design
- Career
- Landscape Architecture
- Construction
- Artificial Intelligence
- Sketching
- Design Softwares
- Diagrams
- Writing
- Architectural Tips
- Sustainability
- Courses
- Concept
- Technology
- History & Heritage
- Future of Architecture
- Guides & How-To
- Projects
- Interior Design
- Competitions
- Jobs
- Store
- Tools
- More
- Home
- Articles
- Architectural Portfolio
- Architectral Presentation
- Inspirational Stories
- Architecture News
- Visualization
- BIM Industry
- Facade Design
- Parametric Design
- Career
- Landscape Architecture
- Construction
- Artificial Intelligence
- Sketching
- Design Softwares
- Diagrams
- Writing
- Architectural Tips
- Sustainability
- Courses
- Concept
- Technology
- History & Heritage
- Future of Architecture
- Guides & How-To
- Projects
- Interior Design
- Competitions
- Jobs
- Store
- Tools
- More
Exploring Different Types of Architectural Roofing Systems for Style and Durability
Discover the diverse world of architectural roofing systems, from traditional gable and hip roofs to modern green and solar designs. Learn about the materials, techniques, and innovations that blend functionality, aesthetics, and sustainability, shaping buildings' identities while addressing environmental and practical demands.

When it comes to architectural design, roofing systems play a pivotal role in both functionality and design. They’re not just about protecting a structure from the elements—they also define its character and enhance its aesthetic appeal. From sleek modern styles to timeless traditional designs, the variety of roofing systems available today offers endless possibilities for creativity and innovation.
As we explore different types of architectural roofing systems, we’ll uncover how they impact durability, energy efficiency, and overall visual appeal. Each system has its unique features, materials, and benefits, making it essential to choose the right one for specific needs. Whether we’re designing a home, a commercial building, or a public space, understanding these options helps us make informed decisions that blend practicality with style. Let’s dive into the fascinating world of roofing systems and discover what makes each one stand out.

Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Architectural Roofing Systems
Architectural roofing systems combine structural integrity with aesthetic design. These systems influence functionality, durability, and visual harmony in buildings. By integrating advanced materials and designs, roofing systems address diverse requirements across residential, commercial, and public construction.
Key elements of architectural roofing systems include slope, material selection, and thermal performance. Slope determines water drainage efficiency; low-slope systems are common in commercial buildings, while steep slopes suit residential spaces. Material choices like metal, asphalt shingles, and clay tiles improve durability under different environmental conditions. High thermal performance materials, such as cool roofing systems, enhance energy efficiency by reducing heat absorption.
Modern roofing technology offers innovative options like green roofs, photovoltaic systems, and structural glazing. Green roofs incorporate vegetation for natural insulation, while photovoltaic systems generate renewable energy. Structural glazing achieves a seamless aesthetic with glass panels while maintaining weather resistance.
Selecting the right roofing system optimizes safety, sustainability, and style. Factors such as building purpose, climate, and budget play a crucial role in the decision-making process.
Traditional Roofing Systems
Traditional roofing systems have shaped architectural styles for centuries, offering a blend of practicality and distinct aesthetics. These systems demonstrate durability and adaptability across climates and regions.
Gable Roofs
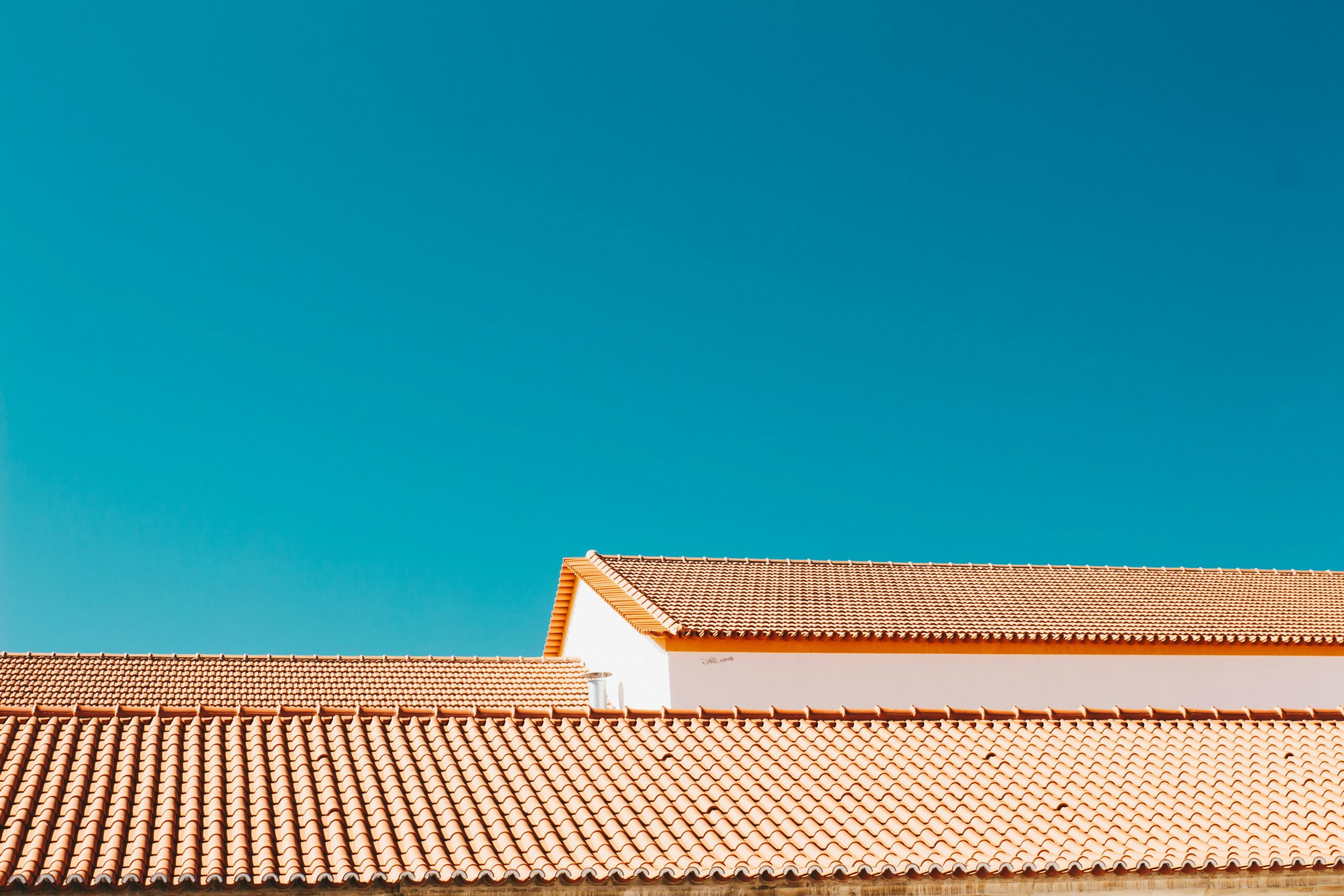
Gable roofs feature two sloping sides that meet at a ridge, creating a triangular shape. They’re widely used due to their simple design, effective water drainage, and cost efficiency. This roof style typically supports materials like asphalt shingles, metal, or clay tiles, which enhance durability. Gable roofs are common in residential architecture, especially in areas prone to heavy rain or snow, as their angle prevents water and snow buildup.
Hip Roofs
Hip roofs consist of four sloping sides that converge at the top, forming a ridge or point. They provide excellent stability and are well-suited for areas with high wind or hurricane exposure. Unlike gable roofs, hip roofing offers uniform eaves on all sides, improving the structure’s balance. Materials like concrete tiles, slate, or wood shingles are often used to create strong and visually appealing hip roofs.
Flat Roofs
Flat roofs are nearly horizontal with a slight pitch to facilitate water drainage. These roofs are popular in modern and commercial architecture due to their sleek appearance and efficient use of space. Flat roofs often support materials like modified bitumen, PVC membranes, or EPDM rubber, which ensure water resistance and durability. They can also serve as spaces for rooftop gardens, solar panels, or recreational uses, promoting sustainability in urban designs.

Modern Roofing Systems
Modern roofing systems integrate innovative technologies and sustainable practices with architectural design. These systems enhance environmental performance and provide functional and aesthetic benefits.
Green Roofs
Green roofs, also known as living roofs, feature vegetation layers installed over waterproof membranes. These systems improve insulation, reduce urban heat, and enhance air quality. Intensive green roofs accommodate deeper soil layers and larger plants, while extensive ones use lightweight materials and require minimal maintenance. Cities like Chicago and Singapore have adopted green roofs for energy savings and biodiversity conservation.
Solar Roofing
Solar roofing incorporates photovoltaic (PV) panels or solar shingles to generate renewable energy. These systems lower electricity costs and contribute to reduced carbon emissions. Solar shingles, designed to resemble traditional roofing materials, offer a seamless aesthetic. Tesla and GAF Energy lead innovations in this domain, enabling homeowners and businesses to integrate energy solutions without compromising roof design.
Membrane Roofing
Membrane roofing consists of single-ply materials like EPDM (ethylene propylene diene terpolymer), TPO (thermoplastic polyolefin), or PVC (polyvinyl chloride). Known for durability and energy efficiency, these systems are widely used in flat or low-slope structures. For example, TPO reflects sunlight, reducing cooling costs in commercial buildings, while EPDM provides flexibility and weather resistance. Prefabrication and installation techniques further enhance performance and longevity.

Materials Used In Roofing Systems
Roofing materials determine durability, energy efficiency, and aesthetics. Their selection affects the structure’s overall performance and adaptation to environmental conditions.
Metal Roofing
Metal roofing offers durability and resistance to extreme weather conditions. Common materials include steel, aluminum, and copper. Steel is often galvanized or coated to prevent corrosion, making it ideal for harsh climates. Aluminum is lightweight and naturally resistant to rust, while copper provides a distinctive appearance and patina over time. These materials can last 40–70 years, with proper maintenance, and reflect sunlight, enhancing energy efficiency. In case of unexpected damage, homeowners can rely on one of many trusted metal roof repair companies to restore functionality. Regular inspections further extend the service life of metal roofing systems.
Asphalt Shingles
Asphalt shingles are cost-effective and widely used in residential buildings. They consist of a fiberglass or organic base coated with asphalt and mineral granules. Fiberglass shingles are more fire-resistant, while organic shingles offer better flexibility in colder climates. Lifespans range from 20–30 years, depending on quality and installation. Their versatility allows for numerous design options, including architectural or 3-tab alternatives.
Clay and Concrete Tiles
Clay and concrete tiles provide timeless aesthetics and robust performance. Clay tiles, fired at high temperatures, resist fading, moisture, and fire. Concrete tiles, made with sand, cement, and water, are heavier but more affordable than clay. Both materials excel in hot climates by offering natural thermal insulation. Lifespans often exceed 50 years, and they are environmentally friendly due to their recyclable nature.

Factors to Consider When Choosing a Roofing System
Choosing a roofing system involves balancing functionality, design, and long-term performance. Evaluating key factors ensures the system aligns with environmental, aesthetic, and financial requirements.
Climate and Weather
Roofing systems must withstand specific climate conditions to ensure durability. In regions with heavy rainfall or snow, steep-slope systems like gable roofs provide efficient drainage. Hot climates benefit from materials like clay tiles, which reflect heat, while metal roofing handles extreme temperature fluctuations well. For areas prone to high winds, hip roofs offer greater stability than flat or low-slope options.
Aesthetic Appeal
A roofing system can define a building’s visual identity when integrated seamlessly with its architectural style. For traditional designs, clay tiles or wooden shingles enhance charm and authenticity. Modern architectures often incorporate metal or membrane roofing for their sleek and minimalist appearance. Customizing colors, textures, and patterns enables a cohesive look that complements surrounding structures and enhances curb appeal.
Budget and Maintenance
Balancing upfront costs with long-term maintenance ensures cost-effectiveness. Asphalt shingles remain an affordable option for residential structures, while metal roofs, although pricier, reduce long-term expenses with minimal upkeep and extended lifespans. Roofing materials like concrete tiles require regular inspections and repairs, increasing maintenance costs over time. Analyzing life cycle costs is essential for making budget-conscious decisions.
Conclusion
Architectural roofing systems play a critical role in defining a building’s functionality, durability, and visual appeal. Examining traditional options like gable, hip, and flat roofs highlights their adaptability to various climates and aesthetic needs. Modern innovations such as green roofs, solar roofing, and membrane systems showcase advancements in energy efficiency and sustainable architecture. Materials like metal, asphalt shingles, and clay tiles further influence the performance and design of these systems, offering distinct advantages based on the structure’s requirements.
Balancing factors like climate, aesthetics, budget, and maintenance ensures the right roofing system aligns with both practical needs and architectural vision. By understanding the unique features and benefits of different roofing types, we can make informed decisions that harmonize style with functionality in any architectural project.
- Architectural roofing systems
- best roofing materials
- custom roofing systems
- durability in roofing
- durable roofing options
- green roofing systems
- innovative roof structures
- modern roofing designs
- roofing for architectural homes
- roofing style inspiration
- roofing style options
- roofing styles and designs
- solar roofing systems
- sustainable roofing solutions
- types of roofing systems
- unique roofing solutions
Submit your architectural projects
Follow these steps for submission your project. Submission FormLatest Posts
Simple and Stylish Roof Ideas for Homeowners
When designing your home, don’t overlook the roof. It’s essential for both...
Key Qualities to Look For in a Residential Roofing Contractor
Choosing a residential roofing contractor involves careful consideration. The roof is a...
Top Signs It’s Time to Replace Your Gutters, Not Just Repair Them
What plays a crucial role in protecting your roof down to the...
From Planning to Completion: Steps for a Successful Roof Project
Undertaking a roofing project can be a daunting experience. Whether you are...











Leave a comment