- Home
- Articles
- Architectural Portfolio
- Architectral Presentation
- Inspirational Stories
- Architecture News
- Visualization
- BIM Industry
- Facade Design
- Parametric Design
- Career
- Landscape Architecture
- Construction
- Artificial Intelligence
- Sketching
- Design Softwares
- Diagrams
- Writing
- Architectural Tips
- Sustainability
- Courses
- Concept
- Technology
- History & Heritage
- Future of Architecture
- Guides & How-To
- Art & Culture
- Projects
- Interior Design
- Competitions
- Jobs
- Store
- Tools
- More
- Home
- Articles
- Architectural Portfolio
- Architectral Presentation
- Inspirational Stories
- Architecture News
- Visualization
- BIM Industry
- Facade Design
- Parametric Design
- Career
- Landscape Architecture
- Construction
- Artificial Intelligence
- Sketching
- Design Softwares
- Diagrams
- Writing
- Architectural Tips
- Sustainability
- Courses
- Concept
- Technology
- History & Heritage
- Future of Architecture
- Guides & How-To
- Art & Culture
- Projects
- Interior Design
- Competitions
- Jobs
- Store
- Tools
- More
The Art of Urban Planning: Designing Livable and Sustainable Cities

Table of Contents Show
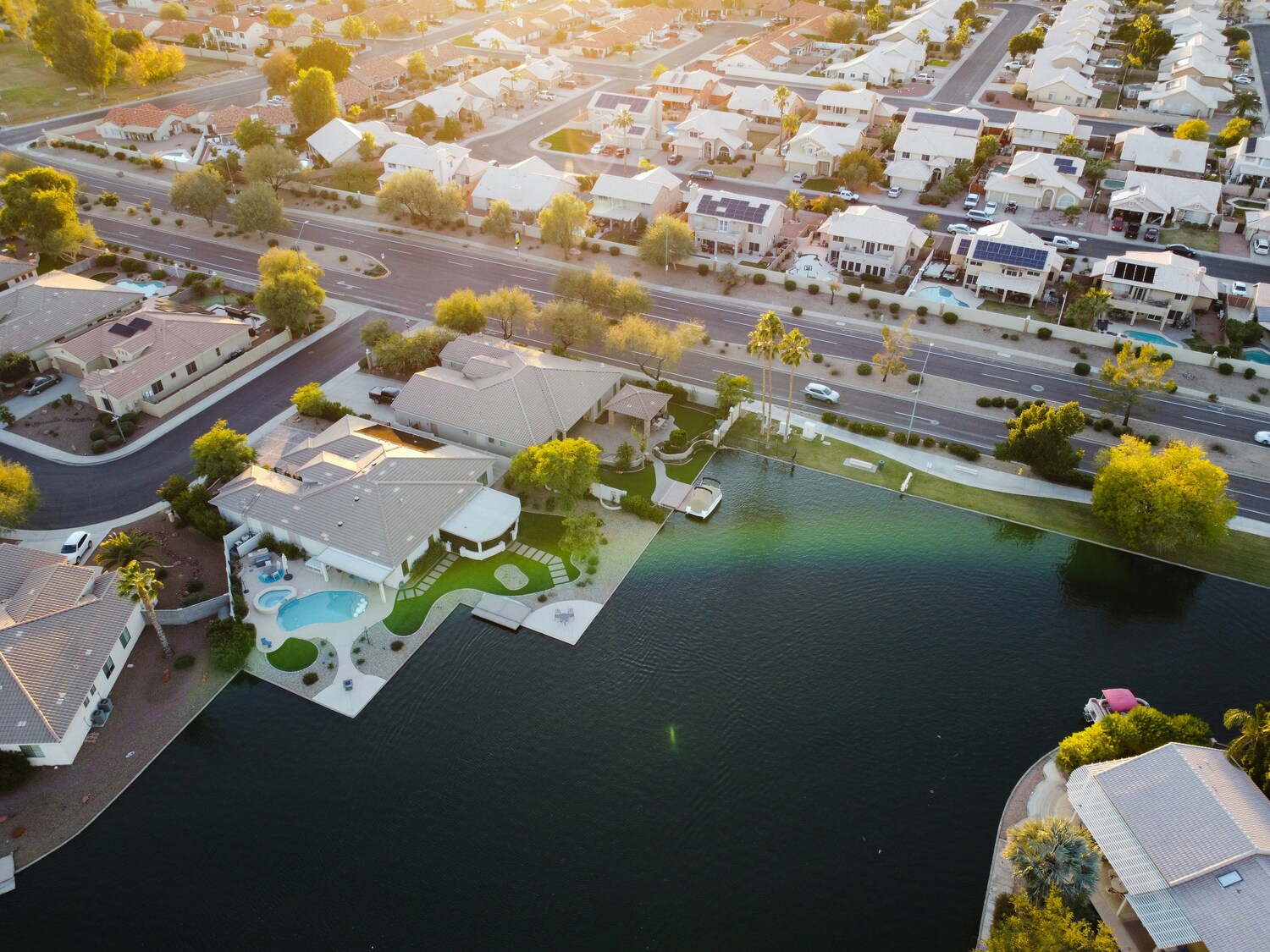
Urban planning is an intricate art form that balances the needs of society with the preservation of our environment, aiming to create cities that are both livable and sustainable. As urban populations continue to grow, the importance of thoughtful urban planning has never been more critical. This blog explores the key principles and strategies that urban planners use to design cities that promote well-being, efficiency, and environmental sustainability.

Understanding the Fundamentals of Urban Planning
Urban planning involves the development and design of land use plans and programs that help create communities, accommodate population growth, and revitalize physical facilities in towns, cities, counties, and metropolitan areas. It is a multidisciplinary practice that incorporates elements of architecture, public policy, sociology, engineering, and environmental science. At its core, urban planning seeks to improve the quality of life for all residents by managing the development of communities in a way that is socially, economically, and environmentally sustainable.
Prioritizing Livability in City Design
Livability is a key focus of urban planning. It refers to the quality of life experienced by the inhabitants of a city. Factors contributing to livability include housing affordability, access to public services, transportation options, public safety, and the availability of green spaces. Urban planners strive to create spaces that are not only functional but also enjoyable to live in. This involves designing pedestrian-friendly neighborhoods, promoting mixed-use developments, and ensuring that essential services and amenities are accessible to all residents.

Embracing Sustainability for Future Generations
Sustainability is another cornerstone of modern urban planning. Sustainable urban design seeks to minimize the environmental impact of cities by conserving resources, reducing pollution, and promoting biodiversity. This includes the integration of green infrastructure, such as parks and green roofs, and the development of sustainable transportation systems that reduce reliance on fossil fuels. Planners also focus on building resilience to climate change by incorporating flood defenses, heat-resistant materials, and other adaptive strategies.
Design the City For All
As urban populations age, the accessibility and inclusivity of cities for elderly residents become increasingly important aspects of urban planning. Creating environments that support the independence, mobility, and well-being of older adults is essential for fostering livable and sustainable cities for all ages. This section explores the key considerations and strategies urban planners use to ensure cities are welcoming and accessible for the elderly. Age-friendly urban design focuses on creating spaces that accommodate the physical and social needs of older adults.

- Enhanced Mobility: Ensuring sidewalks are wide, well-maintained, and obstacle-free to accommodate pedestrians of all abilities, including those using walkers or wheelchairs. Incorporating benches and rest areas at regular intervals can also provide much-needed relief for elderly individuals.
- Safe Transportation Options: Developing reliable and accessible public transportation systems that cater to the needs of older adults. This includes low-floor buses, priority seating, and easy-to-navigate transit stations with clear signage.
- Accessible Housing: Promoting housing options that are adaptable, accessible, and close to essential services and amenities. This can involve the development of senior living communities
The art of urban planning is about much more than simply designing spaces; it’s about creating environments that enhance the quality of life for everyone. By prioritizing livability and sustainability, urban planners play a crucial role in shaping the future of our cities. As we continue to face the challenges of urbanization and climate change, the principles of urban planning will be instrumental in guiding us towards the development of more resilient, inclusive, and sustainable urban environments. Through innovative design and collaborative decision-making, we can build cities that not only meet our present needs but also preserve the planet for future generations.

Submit your architectural projects
Follow these steps for submission your project. Submission FormLatest Posts
Architecture Plan: Tips for Creating & Presenting Plans
Learn how to create and present professional architectural plans with this comprehensive...
Federico Babina Archiplan: Floor Plans of Famous Architects
Federico Babina's ARCHIPLAN series transforms the floor plans of 25 master architects...
10 Essential Things to Consider When Designing a Floor Plan for Your Space
Discover the art of crafting the perfect floor plan in our latest...
How Elevations, Floor Plans, and Sections Work Together in Building Design
Table of Contents Show 1. Visualising the Project from Multiple Perspectives2. Linking...











Leave a comment