- Home
- Articles
- Architectural Portfolio
- Architectral Presentation
- Inspirational Stories
- Architecture News
- Visualization
- BIM Industry
- Facade Design
- Parametric Design
- Career
- Landscape Architecture
- Construction
- Artificial Intelligence
- Sketching
- Design Softwares
- Diagrams
- Writing
- Architectural Tips
- Sustainability
- Courses
- Concept
- Technology
- History & Heritage
- Future of Architecture
- Guides & How-To
- Art & Culture
- Projects
- Interior Design
- Competitions
- Jobs
- Store
- Tools
- More
- Home
- Articles
- Architectural Portfolio
- Architectral Presentation
- Inspirational Stories
- Architecture News
- Visualization
- BIM Industry
- Facade Design
- Parametric Design
- Career
- Landscape Architecture
- Construction
- Artificial Intelligence
- Sketching
- Design Softwares
- Diagrams
- Writing
- Architectural Tips
- Sustainability
- Courses
- Concept
- Technology
- History & Heritage
- Future of Architecture
- Guides & How-To
- Art & Culture
- Projects
- Interior Design
- Competitions
- Jobs
- Store
- Tools
- More
How the BIM Industry is Transforming Modern Construction Practices for a Better Future
Discover how Building Information Modeling (BIM) is revolutionizing the construction industry by enhancing collaboration, reducing costs, and driving sustainability. Explore its benefits, challenges, and the role of emerging technologies like AI and VR in shaping the future of modern construction practices for greater efficiency and innovation.

The construction industry’s evolving, and we’re witnessing a game-changer: Building Information Modeling (BIM). This innovative technology is reshaping how we design, plan, and execute construction projects, making processes smarter, faster, and more efficient. It’s not just about creating 3D models; it’s about driving collaboration and precision across every phase of a project.
With BIM, we’re breaking down silos and fostering real-time communication among architects, engineers, and contractors. It’s revolutionizing workflows by integrating data and insights that help us make better decisions, reduce costs, and minimize errors. The result? Safer, more sustainable structures that meet the demands of modern construction.
As the industry embraces digital transformation, BIM is becoming the backbone of smart building practices. It’s not just a trend; it’s a necessity for staying competitive in today’s fast-paced world. Let’s explore how BIM is leading this transformation and shaping the future of construction.

Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding BIM: A Game Changer in Construction
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is redefining how construction projects are planned, executed, and managed. BIM combines advanced 3D modeling with data integration to create a centralized digital representation of a building’s lifecycle, from design to demolition. This comprehensive approach enhances efficiency and collaboration across project teams.

BIM improves design accuracy by identifying potential conflicts early. For example, clashes between electrical and plumbing systems are detected during modeling, avoiding costly changes during construction. Additionally, BIM supports real-time updates, ensuring all stakeholders access the latest project information.
Collaboration is another critical advantage. By providing a shared digital platform, BIM ensures architects, engineers, and contractors work from the same data set, reducing miscommunication. For instance, structural engineers can coordinate their designs with HVAC systems in the planning phase.
BIM also optimizes cost and resource management. We can simulate construction sequences, analyze energy performance, and accurately estimate quantities, leading to reduced waste and better budget control. For instance, material usage can be optimized by evaluating alternatives within the digital model before procurement.
This digital methodology extends beyond construction. Facility managers use BIM for operations and maintenance by accessing detailed information on systems and components. For example, a damaged HVAC unit’s repair history and specifications are readily available through the model.
As BIM adoption grows, it’s transforming industry standards, fostering data-driven decision-making, and shaping the future of construction practices globally.
Key Advancements in the BIM Industry
Building Information Modeling (BIM) drives innovation in construction by redefining processes, workflows, and outcomes. It aligns industry practices with modern demands for efficiency, sustainability, and precision.

Enhanced Collaboration and Communication
BIM centralizes project data on a unified platform, facilitating seamless collaboration across disciplines. By enabling real-time updates, it ensures architects, engineers, and contractors work with the latest information. For example, structural and electrical plans can be coordinated in the same environment, preventing overlaps. This reduces conflicts, accelerates decision-making, and minimizes delays caused by miscommunication.
Streamlined Project Management
BIM automates scheduling and resource allocation by integrating project timelines with 3D models. Through features like 4D scheduling and construction sequencing, project teams can visualize progress and address potential bottlenecks early. Risk management improves when construction scenarios are simulated, enabling proactive adjustments to timeframes or budgets. These efficiencies result in fewer delays and improved allocation of human and material resources.
Improved Design and Visualization
BIM enhances design processes with advanced visualization tools, delivering precise, realistic 3D renderings. These models detect design inconsistencies, such as clashes between MEP systems and structural elements, before construction begins. Design alternatives can be tested through simulations, ensuring optimal choices for structural integrity, aesthetic appeal, and energy performance. Clients and stakeholders benefit from clearer project representations, reducing uncertainty and aligning expectations.
How BIM Is Transforming Modern Construction Practices
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is reshaping construction practices by driving sustainable solutions, optimizing costs, and enhancing safety. Its data-centric approach empowers project stakeholders to create precise, efficient, and innovative structures.
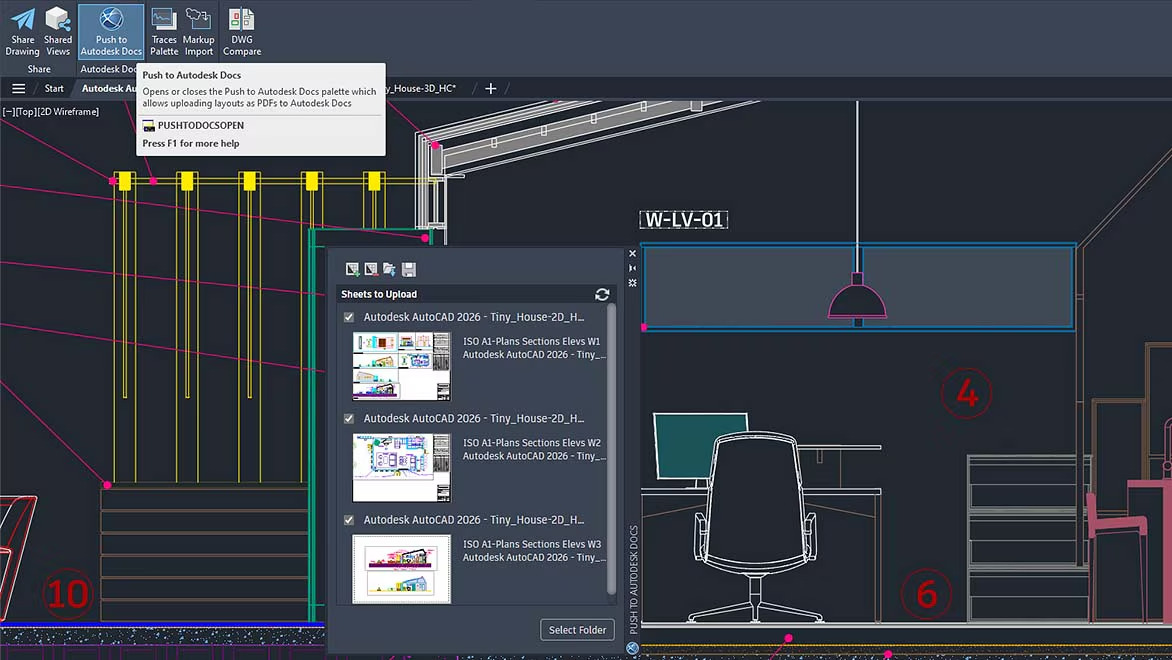
Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Building Solutions
BIM integrates sustainability into construction processes by enabling precise energy performance analysis and resource-efficient designs. With simulation tools, we can evaluate factors like sunlight exposure, thermal performance, and water usage during the design phase. For example, we can assess the environmental impact of materials like concrete and steel before finalizing specifications. BIM also aids in designing energy-efficient systems, such as solar panels and HVAC configurations, enhancing environmental benefits.
Cost Efficiency and Waste Reduction
Cost efficiency improves through BIM’s ability to predict material requirements and construction sequencing. Using BIM, we estimate quantities with over 90% accuracy, minimizing surplus materials that lead to waste. Its 4D simulation capabilities help visualize workflows, identifying inefficiencies and detecting scheduling conflicts proactively. We avoid costly delays by preempting these issues and reducing rework during execution. Real-time budget tracking within BIM platforms ensures strict financial control throughout the project lifecycle.
Risk Mitigation and Better Safety Standards
BIM transforms safety management by allowing thorough risk analysis at every project stage. By simulating construction scenarios, we identify potential hazards and refine safety plans. For instance, virtual models highlight fall risks and collisions in complex structural designs, leading to preventive measures. Improved coordination reduces onsite errors, and BIM-generated safety data supports compliance with regulatory standards. With enhanced visualization, we ensure all teams understand safety protocols, promoting a safer construction environment.
Challenges Facing the BIM Industry
Despite its transformative potential, the BIM industry faces several challenges that hinder its widespread adoption and effective implementation.

Adoption Barriers Across the Sector
Limited standardization, high initial costs, and resistance to change restrict BIM adoption. Many firms operate with traditional workflows that lack integration capabilities with BIM tools. Fragmented industry practices and inconsistent software compatibility create inefficiencies, especially for smaller companies. Additionally, implementing BIM mandates significant financial investment, deterring businesses with limited budgets or uncertain project pipelines. These barriers often delay or dilute the integration of comprehensive BIM workflows across the sector.
Training and Skill Development Needs
A skilled workforce is essential as BIM tools become increasingly complex and specialized. However, there’s a global shortage of professionals proficient in BIM software like Autodesk Revit or Navisworks. Many architects, engineers, and construction managers require upskilling to effectively leverage BIM’s full potential. Without adequate training programs, businesses struggle to align their teams with the evolving digital construction landscape, resulting in underutilization of available technologies and missed opportunities to optimize project performance.
The Future of BIM in Construction
BIM continues to evolve, integrating cutting-edge technologies and responding to global trends that redefine the construction industry. These developments are revolutionizing how we design, build, and manage structures.
Emerging Technologies Enhancing BIM
Artificial intelligence (AI) augments BIM by automating clash detection, optimizing construction schedules, and predicting potential project risks. For instance, AI-driven algorithms analyze datasets from past projects to improve future planning accuracy. Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) enhance design visualization by enabling immersive experiences for stakeholders, providing better design validation before construction begins.
Cloud-based platforms simplify data sharing across teams, ensuring seamless updates and collaboration regardless of location. Additionally, advances in generative design software empower designers to quickly create and test multiple design options, identifying the most efficient solutions. Integration with the Internet of Things (IoT) facilitates real-time monitoring of construction activities and operational systems within structures, improving both performance and safety.
Global Trends Shaping the BIM Industry
Government mandates for BIM adoption are increasing worldwide, driving standardized practices in countries like the UK, Singapore, and Australia. These policies aim to boost transparency and accountability in public construction projects. Sustainability is another major trend, with BIM supporting green building certifications like LEED by providing detailed energy and resource analyses during the design phase.
The rise of 5D BIM, which incorporates cost and time dimensions, is transforming project management by enabling better budget forecasting and scheduling coordination. Global collaboration is also becoming vital as projects involve multidisciplinary teams across different regions. Open BIM standards, such as IFC (Industry Foundation Classes), are addressing software compatibility issues, creating smoother data exchanges. Meanwhile, education programs and training initiatives focus on upskilling professionals to meet growing industry demands.
Conclusion
The BIM industry is redefining modern construction practices by integrating advanced technology, improving collaboration, and driving sustainability. Its ability to centralize project data, optimize resource allocation, and enhance design accuracy is revolutionizing project outcomes across the globe. While challenges such as high costs, skill shortages, and standardization gaps remain obstacles, ongoing advancements like AI, VR, and open BIM are paving the way for broader adoption.
As we embrace digital transformation, BIM establishes itself as a cornerstone of efficiency and innovation in the construction sector.
- BIM adoption
- BIM benefits
- BIM future
- BIM in construction
- BIM industry
- BIM software
- BIM technology
- BIM transformation
- Building Information Modeling
- construction industry trends
- construction innovation
- construction process improvement
- construction project management
- Construction Technology
- digital construction tools
- future of building
- modern construction practices
- smart construction
- sustainable construction
- virtual design construction
Submit your architectural projects
Follow these steps for submission your project. Submission FormLatest Posts
BIM in Architecture: What You Need to Know for Smarter Building Design
Discover how Building Information Modeling (BIM) is transforming architecture with intelligent 3D...
The Future of Architecture: How the BIM Industry Is Changing Design and Construction
Explore how Building Information Modeling (BIM) is revolutionizing architecture with enhanced collaboration,...
The Role of BIM in Revolutionizing Construction Projects: Improving Efficiency and Collaboration
Discover how Building Information Modeling (BIM) is revolutionizing the construction industry by...
Understanding the Impact of BIM on the Construction Industry: Revolutionizing Building Projects
Discover how Building Information Modeling (BIM) is revolutionizing the construction industry by...












Leave a comment