- Home
- Articles
- Architectural Portfolio
- Architectral Presentation
- Inspirational Stories
- Architecture News
- Visualization
- BIM Industry
- Facade Design
- Parametric Design
- Career
- Landscape Architecture
- Construction
- Artificial Intelligence
- Sketching
- Design Softwares
- Diagrams
- Writing
- Architectural Tips
- Sustainability
- Courses
- Concept
- Technology
- History & Heritage
- Future of Architecture
- Guides & How-To
- Art & Culture
- Projects
- Interior Design
- Competitions
- Jobs
- Store
- Tools
- More
- Home
- Articles
- Architectural Portfolio
- Architectral Presentation
- Inspirational Stories
- Architecture News
- Visualization
- BIM Industry
- Facade Design
- Parametric Design
- Career
- Landscape Architecture
- Construction
- Artificial Intelligence
- Sketching
- Design Softwares
- Diagrams
- Writing
- Architectural Tips
- Sustainability
- Courses
- Concept
- Technology
- History & Heritage
- Future of Architecture
- Guides & How-To
- Art & Culture
- Projects
- Interior Design
- Competitions
- Jobs
- Store
- Tools
- More
Top 6 Software Architecture Diagram Secret Tricks Every CS Student Should Know in 2025-26

Table of Contents Show
Read this article to learn simple and effective ways to create software architecture diagrams that support clear visuals and stronger system understanding. You will see how these techniques help Computer Science students improve technical communication and prepare for success in 2025 and 2026.
Have you ever noticed that a simple software architecture diagram explains a system faster than a long block of text? This matters for every CS student because clear visuals support clear thinking. A diagram shows how each part connects and how data moves. It helps you understand a system without stress. A well-organised diagram saves time. A cluttered one creates confusion.
Software architecture diagrams will become more detailed in the coming years as modern systems increasingly use cloud architectures and many small services. A ResearchGate study shows that students understand system workflows faster when they use structured diagrams because clear visuals reduce cognitive load. This trend makes structured diagram design more important. In this article, we will discuss six simple tricks that will improve your software architecture diagrams and your confidence.
Key Insights Of The Article:
- A strong software architecture diagram provides rapid clarity and time-saving through planning.
- The system remains uncomplicated despite its complex shapes and designs.
- Labelling eliminates confusion and guides the viewer to the right parts of the system.
- Regular symbols allow the mind to follow the flow effortlessly.
- A balanced application of colour emphasises what is truly essential in the architecture program diagram.
6 Must-Know Software Architecture Diagram Tricks for CS Students
Start your learning with a clear view of how smart software architecture diagrams guide your technical growth. Just like a trusted assignment writing service, like The Academic Papers UK, helps CS students tackle tough tasks and improve their results, these diagrams give you a clear roadmap to understand complex systems. By mastering the basics first, you set yourself up for faster learning and stronger outcomes.
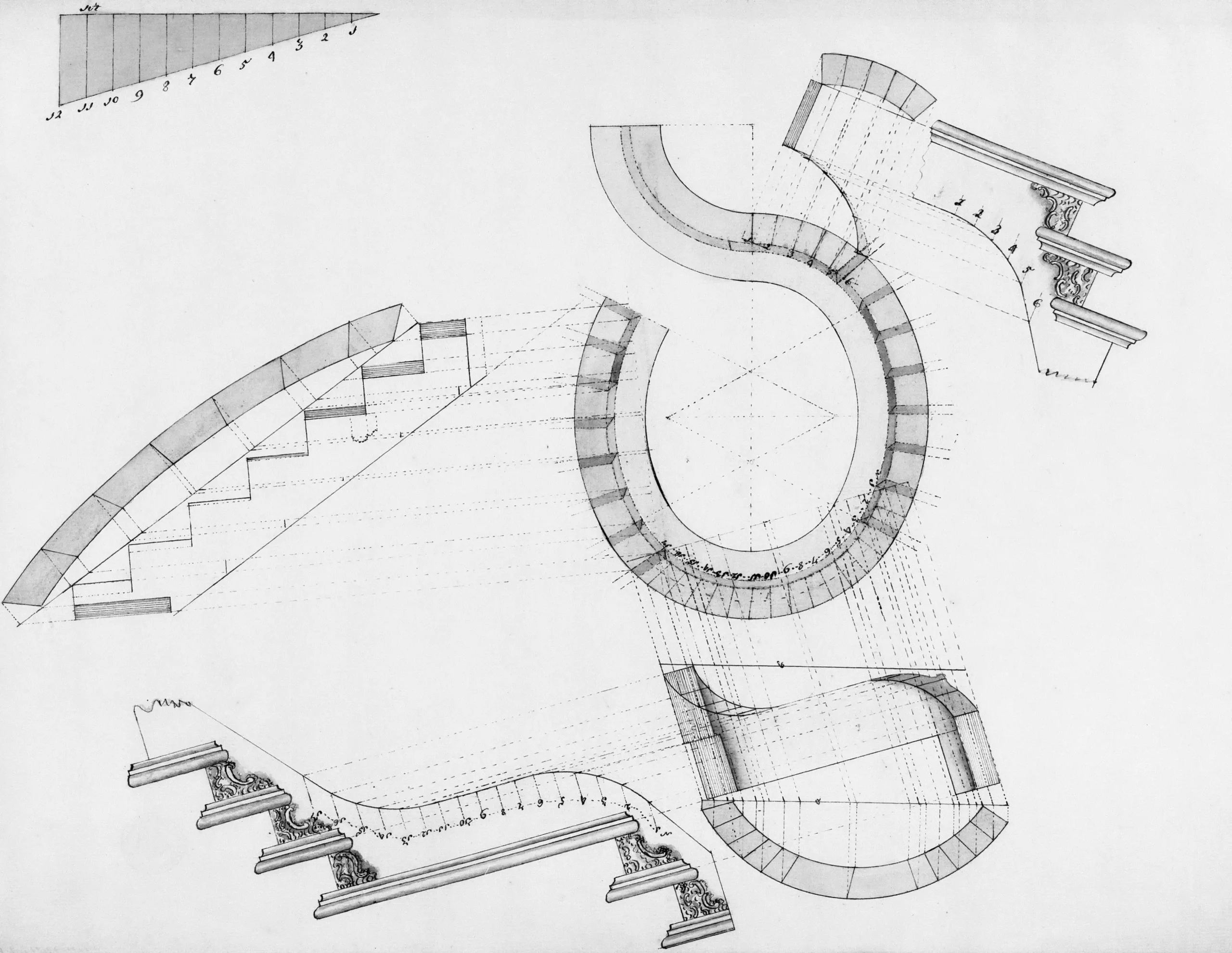
Select the Right Diagram Type for Your Objective
Start with a clear purpose. Ask yourself one question. What do you want the diagram to show? This focus guides every decision you make. Springer Nature reported that clear visual goals improve understanding and reduce design errors. You choose the right data architecture diagram when you know your goal. Each diagram tells a specific story and highlights a different part of the system.
UML Class Diagrams for Structure
Class diagrams must be used to demonstrate structure. These architectural diagrams depict the classes and their interconnections. They help you develop object-oriented systems. They reveal characteristics and procedures
A class architecture diagram tool is applicable during the planning phase of an e-commerce application. You may display such classes as User, Product Order and Cart. This provides the viewer with a clear understanding of how the system is constructed.
Sequence Diagrams for Interactions
Sequence diagrams are used when you are interested in demonstrating interactions. They show the conversations that objects can have with one another over a simple timeline. They excel at explaining a workflow. In the case of a login process, you show the user how the server validates the information. You show the database as it sends results. This simplifies each and every step.
Deployment Diagrams for Runtime Setup
Deployment software architectural diagrams should be used when you are interested in indicating the locations of your system execution. They are used to show runtime nodes and the setup environment. They assist in visualising the behaviour of your system during execution. A cloud environment can be demonstrated using an application server and load balancers. This procedure clarifies the view of runtime.
Example of Using Mixed Diagrams
One diagram is not always sufficient in a web app. You can begin with a component diagram that displays system components. Then put in a sequence diagram to represent the login flow. Both graphs complement one another. They provide the system with a complete picture
Start With a High-Level Overview
Many CS students get into too much detail, which distracts and disrupts their work. A high-level, basic view establishes the right foundation. It helps you focus on the main point. An MIT study indicated that learners comprehend systems quickly when they initially observe the big picture. This technique will make your software architecture diagram understandable.
Top-Down Design Mindset
Top-down design helps divide ideas into smaller parts. Start with the entire system, then break it into modules. Each module is later subdivided into small sections. This progressive dissection assists in having your software architecture diagram expand in a clear manner.
The Advantages of a High-Level Start.
The level starts high and eliminates confusion. The viewer perceives the system as unified. They know the role of every component. This simplifies future explanations of details, making your work look cleaner. The structure of the design will provide more confidence to teachers and teammates.
Use Consistent Symbols, Shapes, and Notation
An effective software architecture diagram is based on consistency. Changes in symbols confuse the viewer. You should choose one style and consistently use it throughout your software diagram. Using symbols makes your message very basic. Software architecture diagrams can also help in writing a visual writing essay by offering a structured approach to planning and visualising the narrative flow and structure
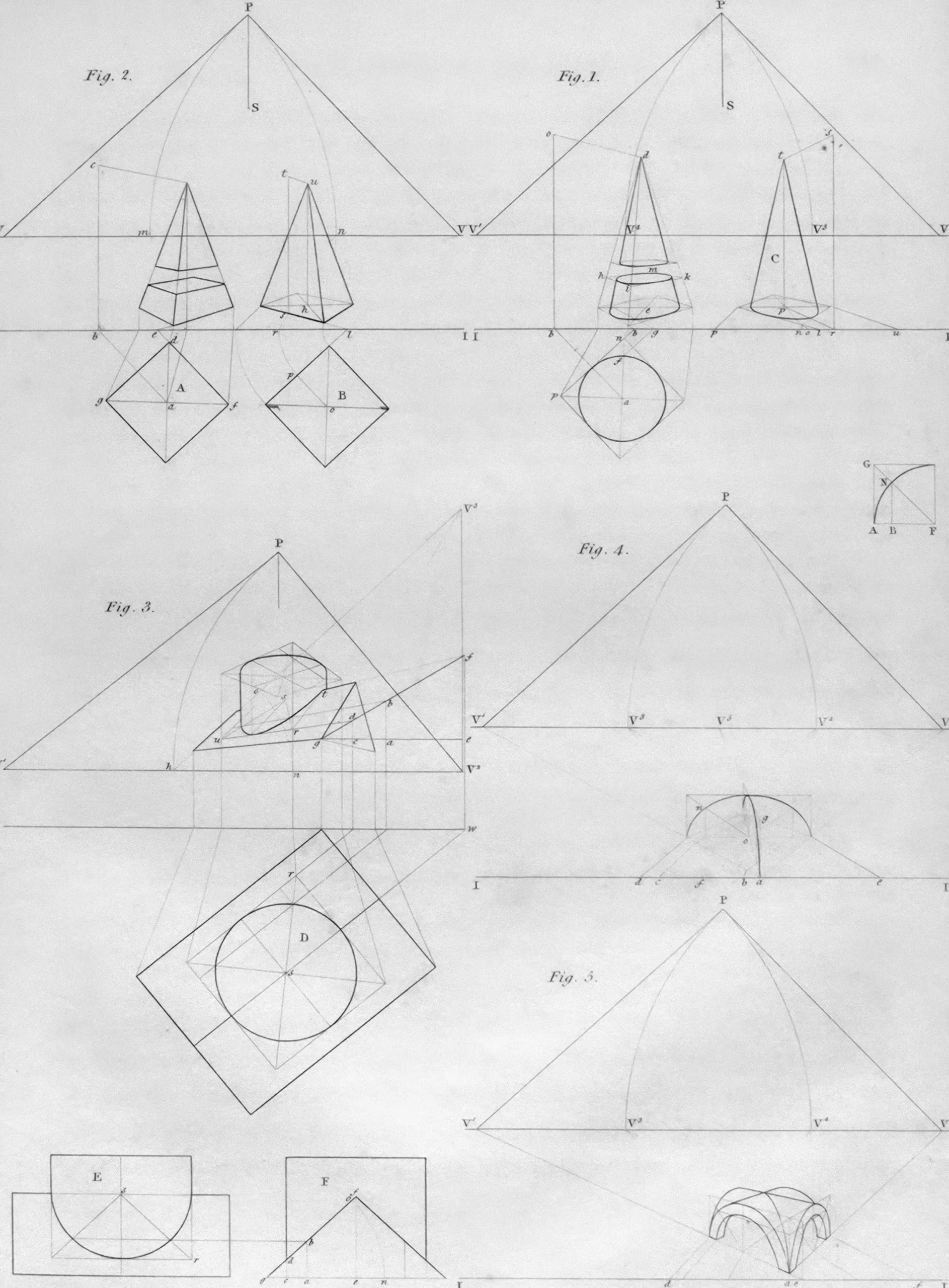
The University of Toronto conducted a study that found that regular images enhance clarity in technical learning. This finding demonstrates the relevance of stable symbols.
Choose One UML Style
Rectangles help you display clear symbols and classes in UML. Arrows can represent flow, and diamonds indicate connections. This strategy creates a smooth flow in your diagram and helps the viewer easily understand each part.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Many students mistake shapes without understanding. They generate comparable circles and squares, which they subsequently use. These habits reduce clarity and help you avoid mistakes. Keep each symbol steady and in a meaningful shape. This procedure is just a basic step that will make your diagram more powerful and easier to read.
Apply Colour Coding Strategically
Applying the colour code to the software architecture diagram plays a significant role. It governs the visual orientation and shapes perceptual processes. However, similar to other tools, it may lead to distractions if employed irresponsibly. The plain colour scheme maintains a concentration of meaning.
Colour for Module Type
Assign a unique colour to each module category.
- Green for front-end activities.
- Blue may be selected as the backend.
- Orange colour highlights the critical path
It is simple to code, and the viewer can understand roles by looking at them. All the colours convey significance without the need for supplementary text.
Colour for Data Flow
Data movement is also displayed using colour. A single colour of user data can be used. You can use more of the system data. This technique makes it easy to understand the flow of information. The viewer understands direction and intent without reading several pages of explanations. Flow is transformed into a visual narrative through simple colour combinations.
Simplify and Avoid Overcrowding
The software architectural diagrams should be clear and easy to understand. You need to show what value is added. Maintain consistency across all aspects of the message. Organise the items in the group in designated areas. Such a strategy eliminates clutter and makes the software architecture diagram easier to read.
Divide Large Systems into Several Diagrams
Within a single framework, extensive systems experience confusion. Exposing a viewer to excessive information can lead to confusion and disorientation. Divide the system into multiple special diagrams. Show the database in a single view. Display user interaction in a separate view. The approach keeps each tier plain and simple to inspect.
Use One Layer per Diagram
Each software architecture diagram should represent a single level of abstraction. The high-level process and the low-level architecture cannot be contained within a single framework. The database tables and mix modules cause the viewer to struggle. Each level should be represented in a different diagram to be clear and accurate.
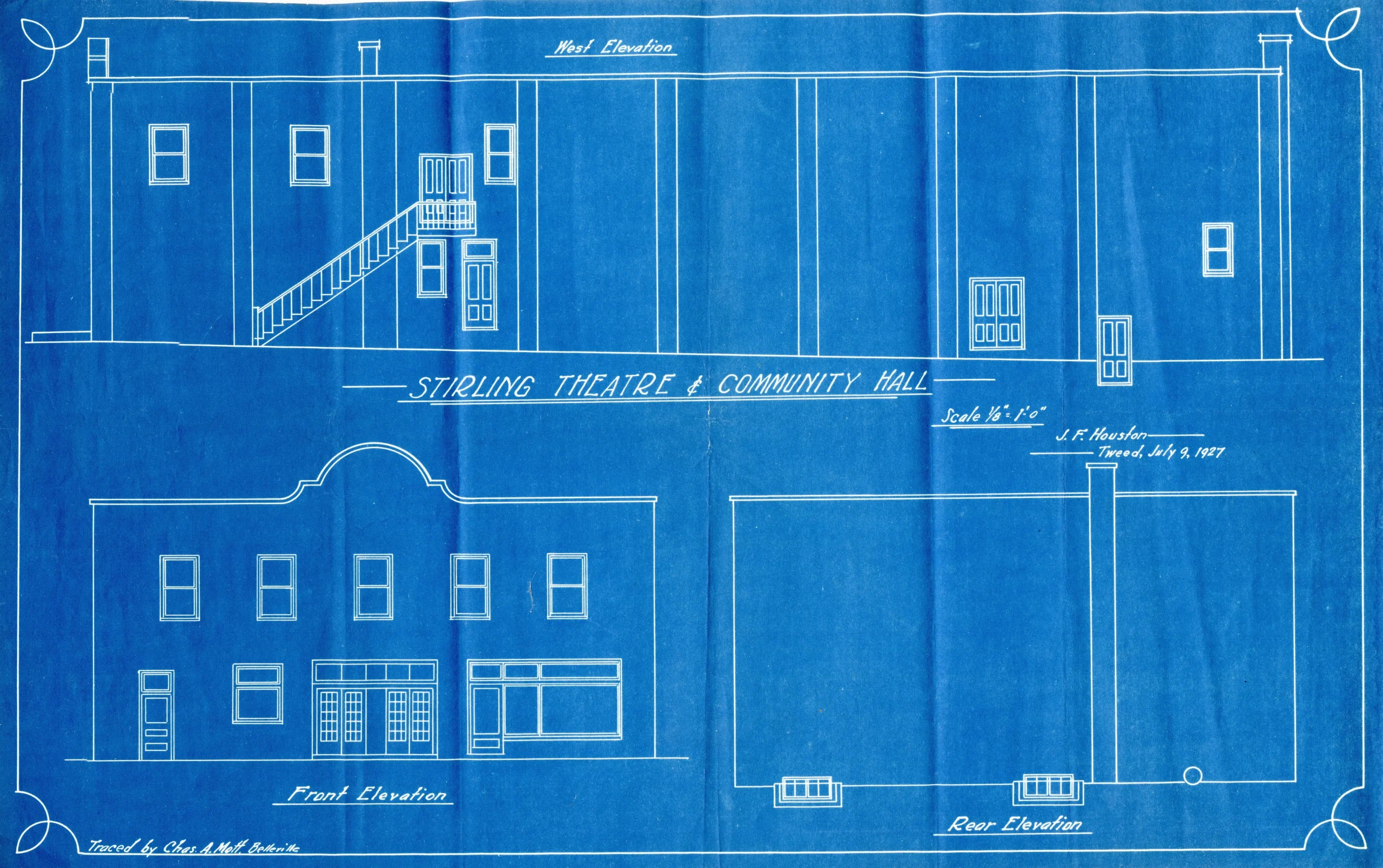
Annotate Key Components Clearly
Every software architecture diagram is strengthened with clear annotations. You provide direct meaning to shapes and symbols in the form of brief notes. You eliminate speculation and steer the viewer in the right direction. When every component is clearly labelled and simple to use, the system is easier to explain without the need for verbal illustrations.
Use Short and Direct Labels
Put short labels on modules to indicate functions and services. Each label should be dedicated to the purpose of the component. It should be expressed in simple language which a new viewer can understand. Minimal descriptions lead to less confusion and facilitate rapid interpretation. The software architecture diagram is also clear and has a short label, making it easy to scan through.
Describe Critical Paths
Provide brief notes indicating the critical paths within the system. The notes guide the viewer through key flows and help them understand how the system handles vital tasks. Their appearance will also help in making the diagram more informative.
How External Guidance Can Help CS Students in Tackling Complex Tasks
Computer Science students often face tight deadlines and challenging assignments that require a deep understanding of complex systems. Just as a well-designed software architecture diagram provides clarity, UK-based assignment writing services can efficiently help students through difficult tasks. Professionals assist CS students by providing systematic explanations, step-by-step solutions, and real examples.
These services can:
- Divide the problem of complex systems and programmes into manageable chunks.
- Make documentation and code samples easy to understand and a best practice.
- Improve academic performance by providing high-quality, plagiarism-free content.
- Offer guidance on presentation and formatting, ensuring work meets university standards.
By integrating professional assistance with your own learning, you gain the dual advantage of understanding core concepts while meeting deadlines.
Conclusion
The best six software architecture diagram tricks of the 2025-26 era equip every CS student with the knowledge they need. The methods help you to be logical and confident in your ideas. When you make your diagrams simple and clean by layer and eliminate visual clutter, you make it easier to understand. Dividing large systems into multiple views will help the viewer explore them.
The habits also make your diagrams look well-organised and professional. Strong diagrams are more than just representations of systems. They show the developer’s proficiency. They support your ability to communicate effectively with groups and facilitate the understanding of complex concepts. Once you master such tricks, you create a skill that will help you throughout your development in each project and career level.
Frequently Asked Questions About Software Architecture Diagrams
What is a Software Architecture Diagram?
A software architecture diagram illustrates how a system works. It shows the system’s key components. It illustrates how these sections relate to each other. It allows you to visualise the data flow. It also helps you understand the role of each part. This diagram is used to guide development teams. It reduces confusion. It provides a distinct image of the entire building. Many teams use it to plan work.
What Are 3 Types of Architecture?
There are three types of architecture, which describe a three-layered system.
- The first layer is the presentation layer. It manages the user’s interface.
- The second layer is the logic layer. It manages rules and actions.
- The third one is the data layer. It retains and retrieves information.
Such a system facilitates simple system management. It also makes changes simple. Each layer has a clear job. This arrangement is prevalent in contemporary apps. Many developers use this arrangement because it keeps their work organised and straightforward.
What Are the 4 C’s of Architecture?
The four Cs help you gain a simple understanding of a system.
- The first C is Context. It demonstrates how the system fits into the world.
- The second C is Containers. It demonstrates the grand sections within the system.
- The third C is Components. It demonstrates the way to plan the items within the group.
- The fourth C is Code. It shows the final details.
This model provides a clear picture on every level. It helps teams stay on track. It also helps in improved planning and design.
illustrarch is your daily dose of architecture. Leading community designed for all lovers of illustration and drawing.
Submit your architectural projects
Follow these steps for submission your project. Submission FormLatest Posts
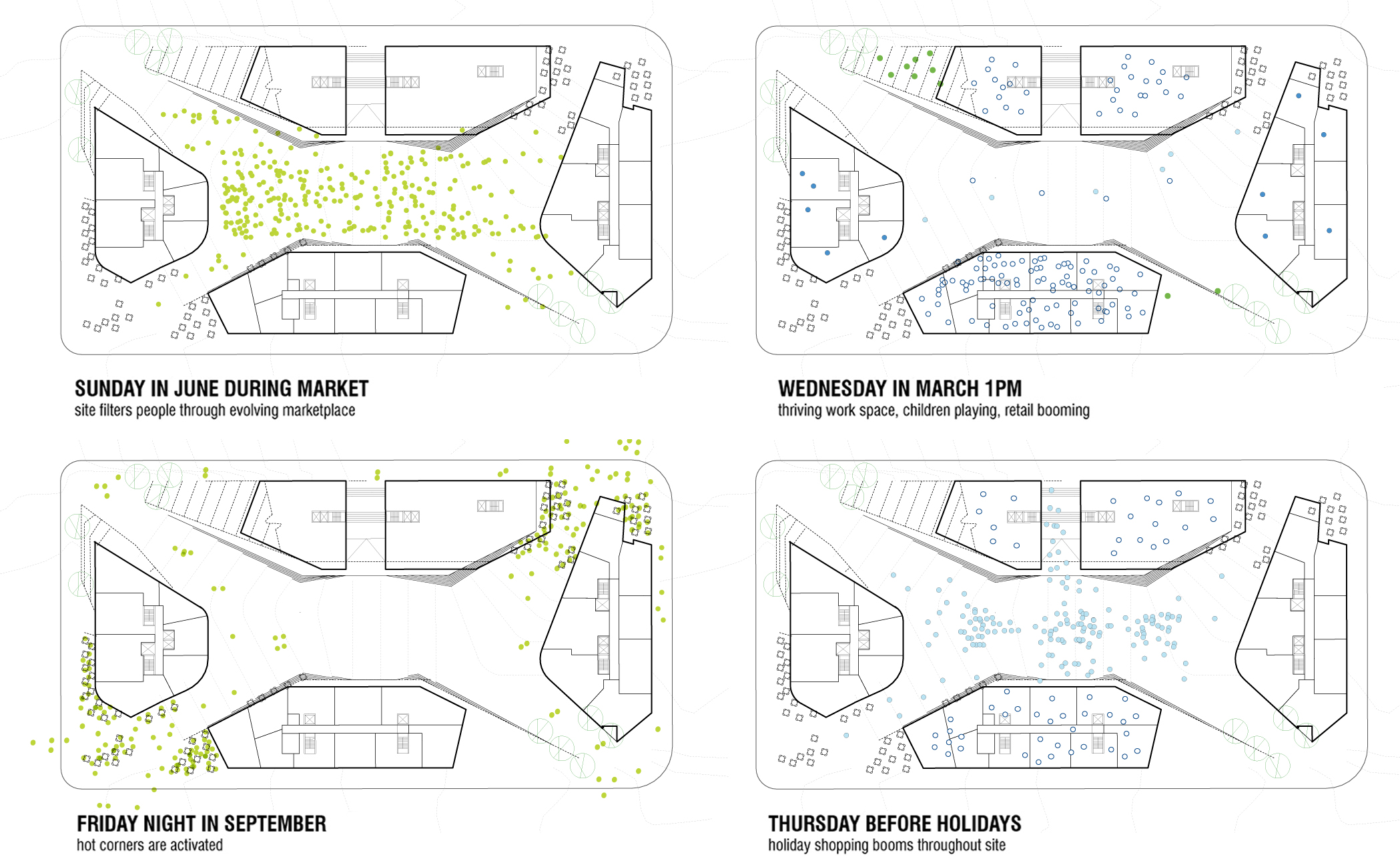
Understanding Architectural Bubble Diagrams: A Complete Guide
Architectural bubble diagrams are foundational space-planning tools that map functional relationships between...
Understanding the Role of Bubble Diagrams in Modern Architecture Design
Explore the fascinating role of bubble diagrams in modern architecture, a vital...
Architecture Circulation Diagram: Guide to Movement & Flow Design
A circulation diagram in architecture is a visual tool that maps how...
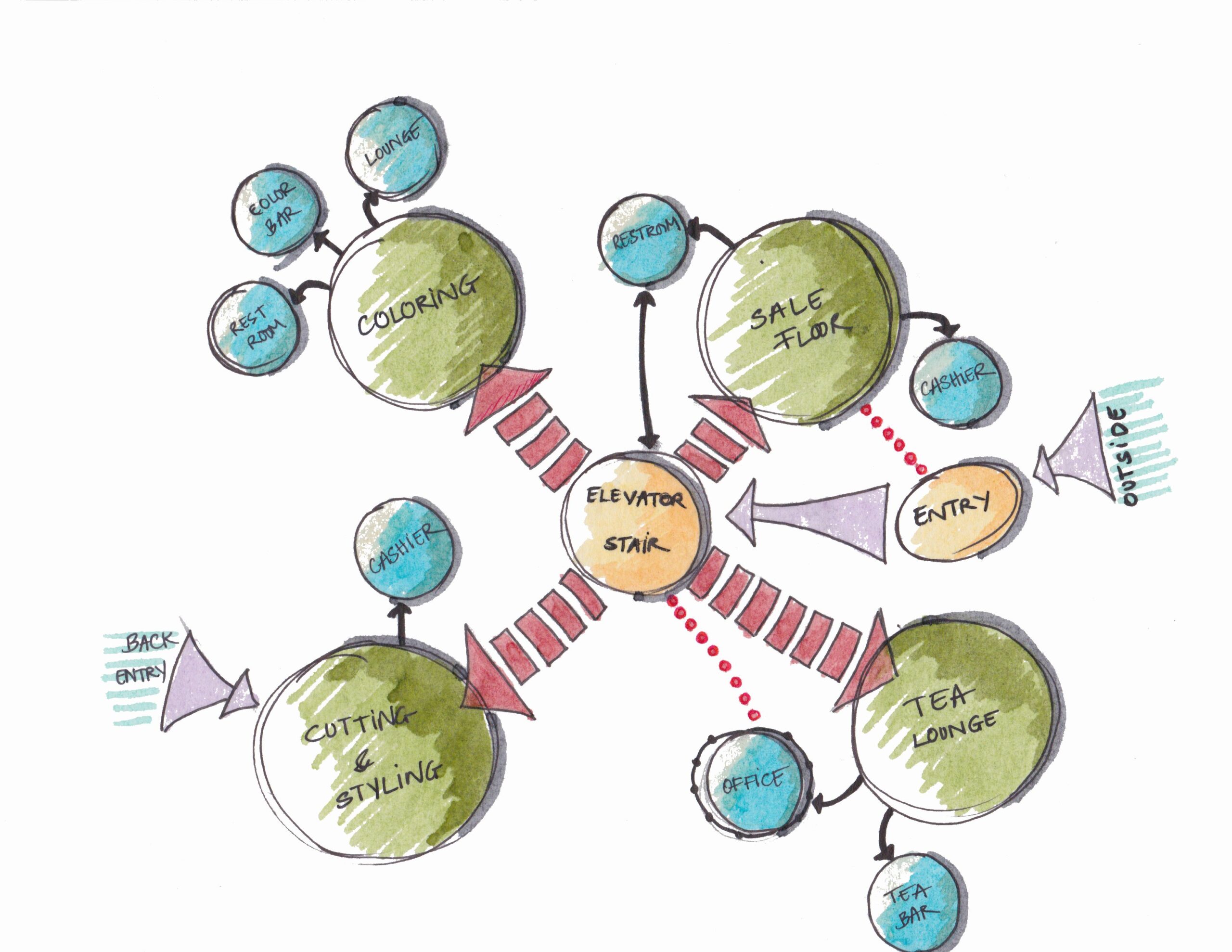
Bubble Diagram In Architecture
Bubble diagrams are essential tools in the early stages of architectural design,...









Leave a comment