- Home
- Articles
- Architectural Portfolio
- Architectral Presentation
- Inspirational Stories
- Architecture News
- Visualization
- BIM Industry
- Facade Design
- Parametric Design
- Career
- Landscape Architecture
- Construction
- Artificial Intelligence
- Sketching
- Design Softwares
- Diagrams
- Writing
- Architectural Tips
- Sustainability
- Courses
- Concept
- Technology
- History & Heritage
- Future of Architecture
- Guides & How-To
- Art & Culture
- Projects
- Interior Design
- Competitions
- Jobs
- Store
- Tools
- More
- Home
- Articles
- Architectural Portfolio
- Architectral Presentation
- Inspirational Stories
- Architecture News
- Visualization
- BIM Industry
- Facade Design
- Parametric Design
- Career
- Landscape Architecture
- Construction
- Artificial Intelligence
- Sketching
- Design Softwares
- Diagrams
- Writing
- Architectural Tips
- Sustainability
- Courses
- Concept
- Technology
- History & Heritage
- Future of Architecture
- Guides & How-To
- Art & Culture
- Projects
- Interior Design
- Competitions
- Jobs
- Store
- Tools
- More
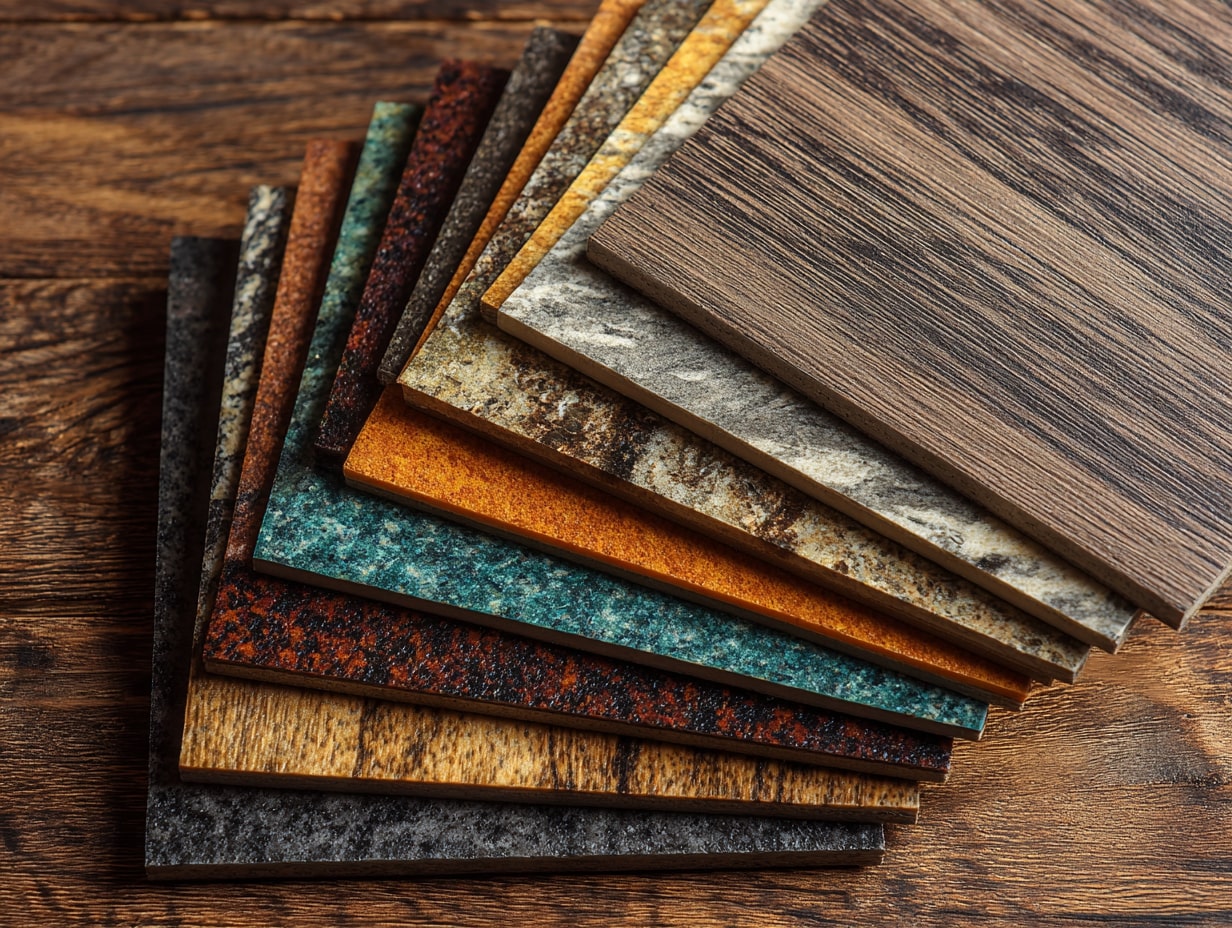
Top Sustainable Surface Materials Every Designer Should Know
Explore sustainable surface materials with a designer-ready scorecard: carbon, toxins, durability, circularity, plus EPD/HPD, FSC, and low‑VOC install tips.
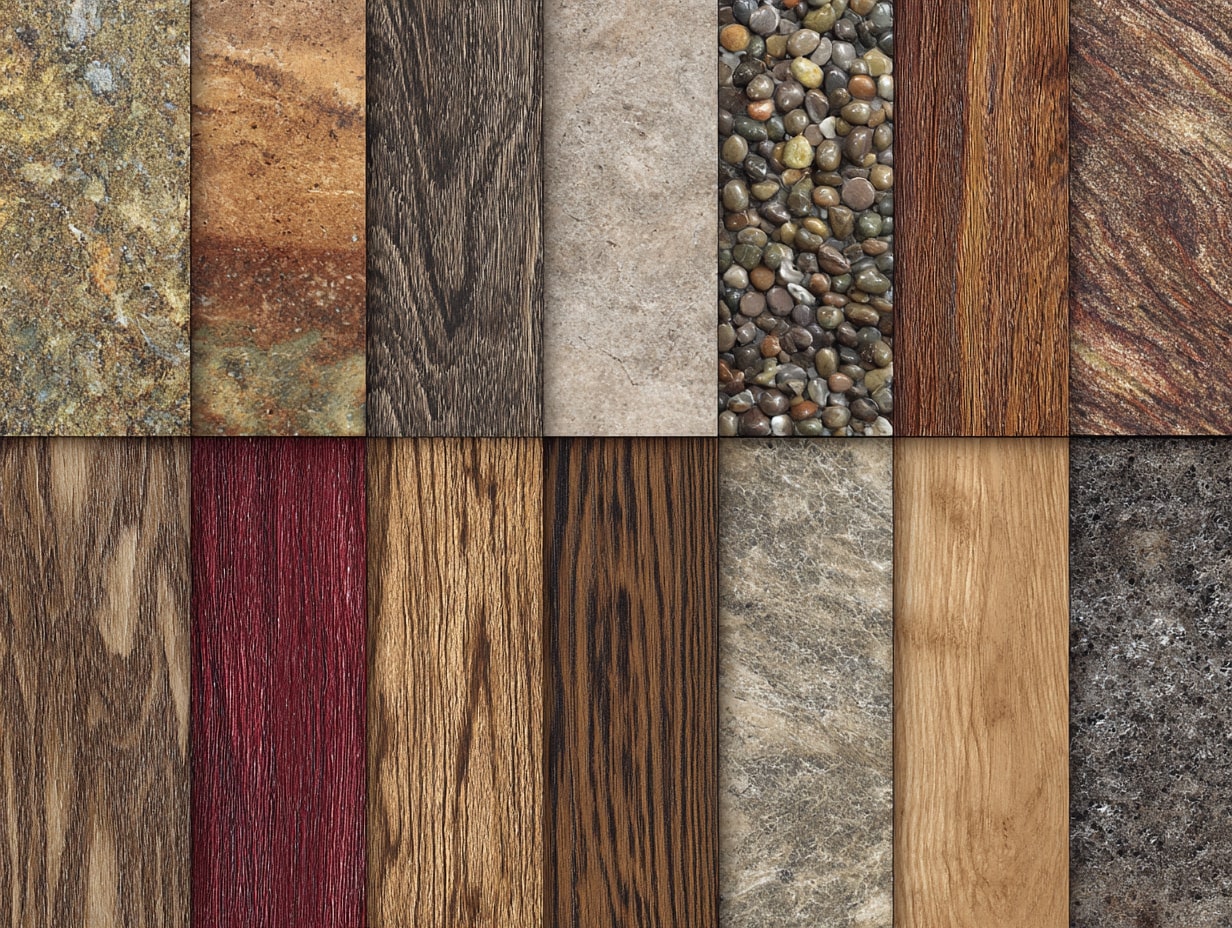

Clients are asking harder questions about what goes into their spaces, and we should too. When we evaluate sustainable surface materials, we’re balancing aesthetics with embodied carbon, health, and long-term performance. Here’s how we make smart, durable choices without sacrificing design intent.
Table of Contents
ToggleHow To Evaluate Sustainable Surface Materials
Core Criteria: Embodied Carbon, Durability, Toxins, And Circularity
We start with a quick scorecard: embodied carbon (use EPD data or manufacturer LCAs), expected lifespan, and maintenance intensity. Then we assess toxins, no added formaldehyde, low-VOC, and Red List avoidance. Finally, circularity: recycled content, repairability, and realistic end-of-life pathways.
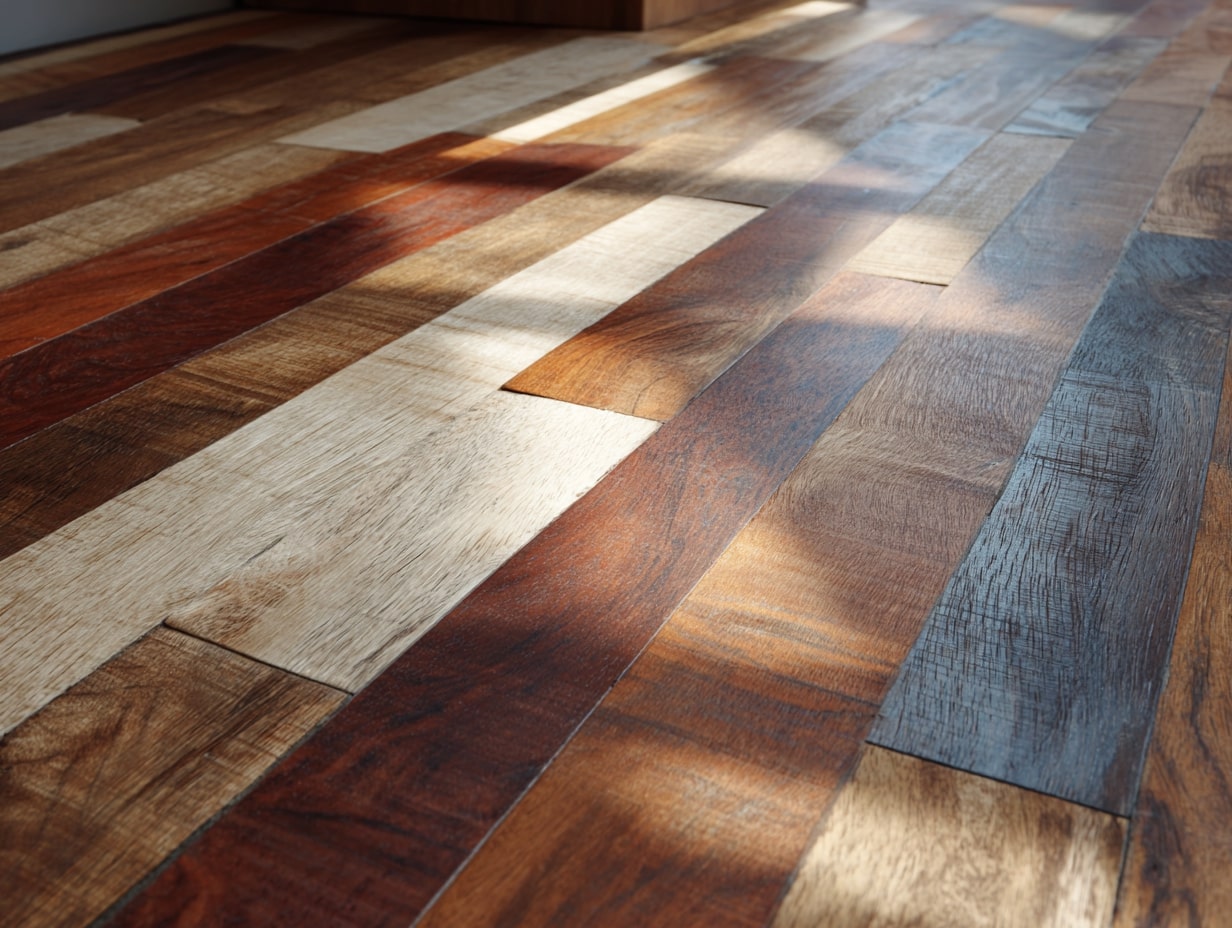

Certifications And Transparency: EPD, HPD, FSC, FloorScore, And Cradle To Cradle
An EPD quantifies impacts: an HPD discloses ingredients. For wood, we prioritize FSC. For indoor air quality, FloorScore or GREENGUARD helps. Cradle to Cradle goes further, material health, circular design, renewable energy, use it to differentiate truly sustainable surface materials.
Installation And Maintenance: Low-VOC Adhesives, Finishes, And Care
Great materials can be ruined by toxic install kits. We specify water-based, low-VOC adhesives and finishes, verify SCAQMD Rule 1168 compliance, and prefer mechanical fastening where possible. Maintenance plans matter too, neutral cleaners, spot-repair options, and finish renewal extend life and lower impact.
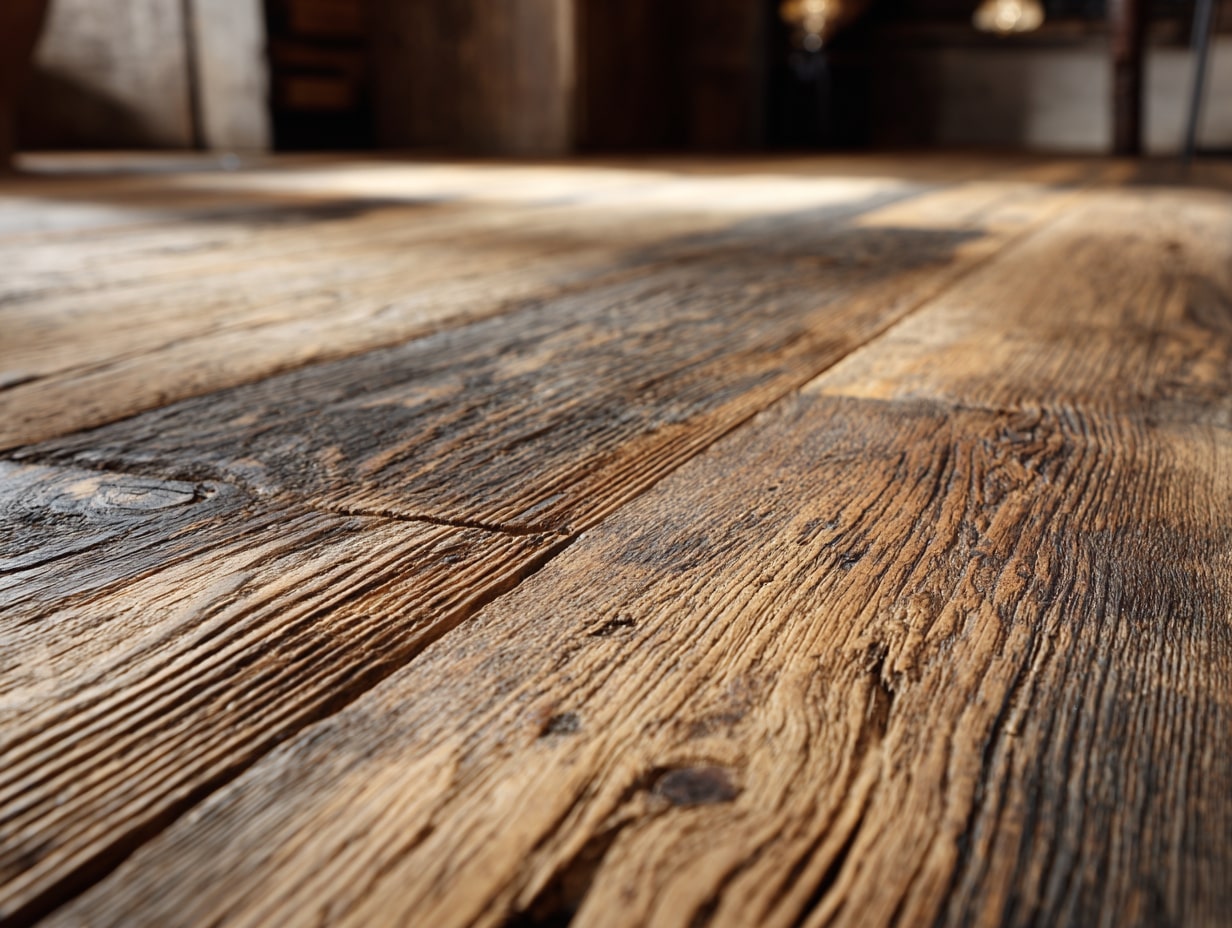
Wood, Bamboo, And Cork: Renewable Natural Surfaces
FSC-Certified Wood And Modified Timber For Wet Zones
We lean on FSC-certified hardwoods and softwoods for traceability and forest stewardship. In wet or exterior-adjacent areas, acetylated or thermally modified wood offers durability without heavy metals. Specify no- or low-formaldehyde binders and hardwax oils for maintainable protection.

Bamboo: Rapidly Renewable With Density And Adhesive Considerations
Bamboo grows fast and performs well when strand-woven (dense, hard) or cross-laminated for stability. The catch is adhesives, look for low-emitting, phenol-formaldehyde–free options and third-party air-quality certifications. Edge protection and acclimation reduce cupping and surface bruising.
Cork: Thermal Comfort, Acoustic Benefits, And Finish Options
Cork provides cushioned feel, warmth, and excellent NRC. It’s harvested without felling trees, which supports biodiversity. For durability, we specify factory-cured finishes or site-applied waterborne poly. In kitchens, choose higher-density cork and mats at work zones.
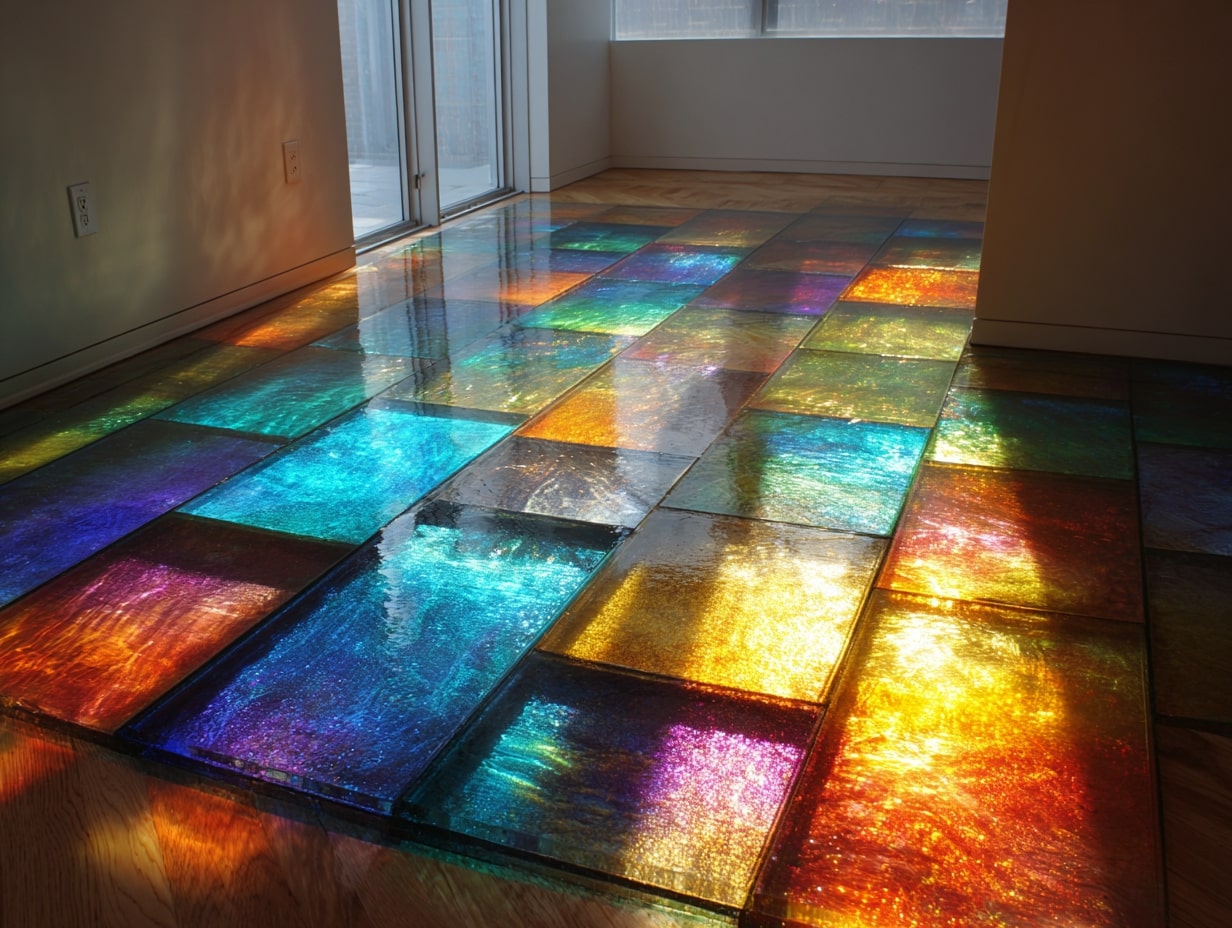
Recycled And Upcycled Composites: Glass, Paper, And Metal
Recycled Glass Slabs And Terrazzo: High Recycled Content And Visual Depth
Recycled glass surfaces deliver striking colorways with post-consumer content often above 70%. Terrazzo, cementitious or epoxy, handles high traffic and can incorporate regional aggregates. Plan for slab support, compatible sealers, and end-of-life pathways such as re-crushing as aggregate.

Paper Composite Surfaces: Warm Tactility, Food-Safe Resins, And Repairability
Phenolic-free or low-formaldehyde paper composites offer a warm, matte touch and are popular for worktops and fixtures. Many are food-safe once cured and can be refinished like wood. We detail eased edges and specify breathable finishes to avoid ghosting.
Aluminum And Steel Panels: Post-Consumer Content And Infinite Recyclability
Aluminum and steel boast high recycling rates and theoretically infinite loops. Ask for documented post-consumer percentages and mill certifications. Powder-coat finishes minimize solvents: for exterior, select marine-grade alloys or galvanized/SS options to avoid premature replacement.
Mineral-Based Options: Ceramic, Porcelain, And Sintered Stone
Tile With Recycled Content: Low VOC, High Wear, And Responsible Glazes
Porcelain and ceramic tile are inert, low-VOC, and tough. Many manufacturers offer 20–40% recycled content plus EPDs. We check glaze chemistry for heavy metals and specify low-VOC grouts and sealers. Modular sizes and rectified edges reduce waste during install.
Sintered/Ultracompact Surfaces: Heat Resistance, UV Stability, And End-Of-Life
Sintered slabs perform under heat, UV, and abrasion, great for kitchens and exteriors. They’re largely mineral, with no resins, which reduces VOCs. Plan cut strategies to limit waste and confirm local recyclers that accept crushed slabs as aggregate.
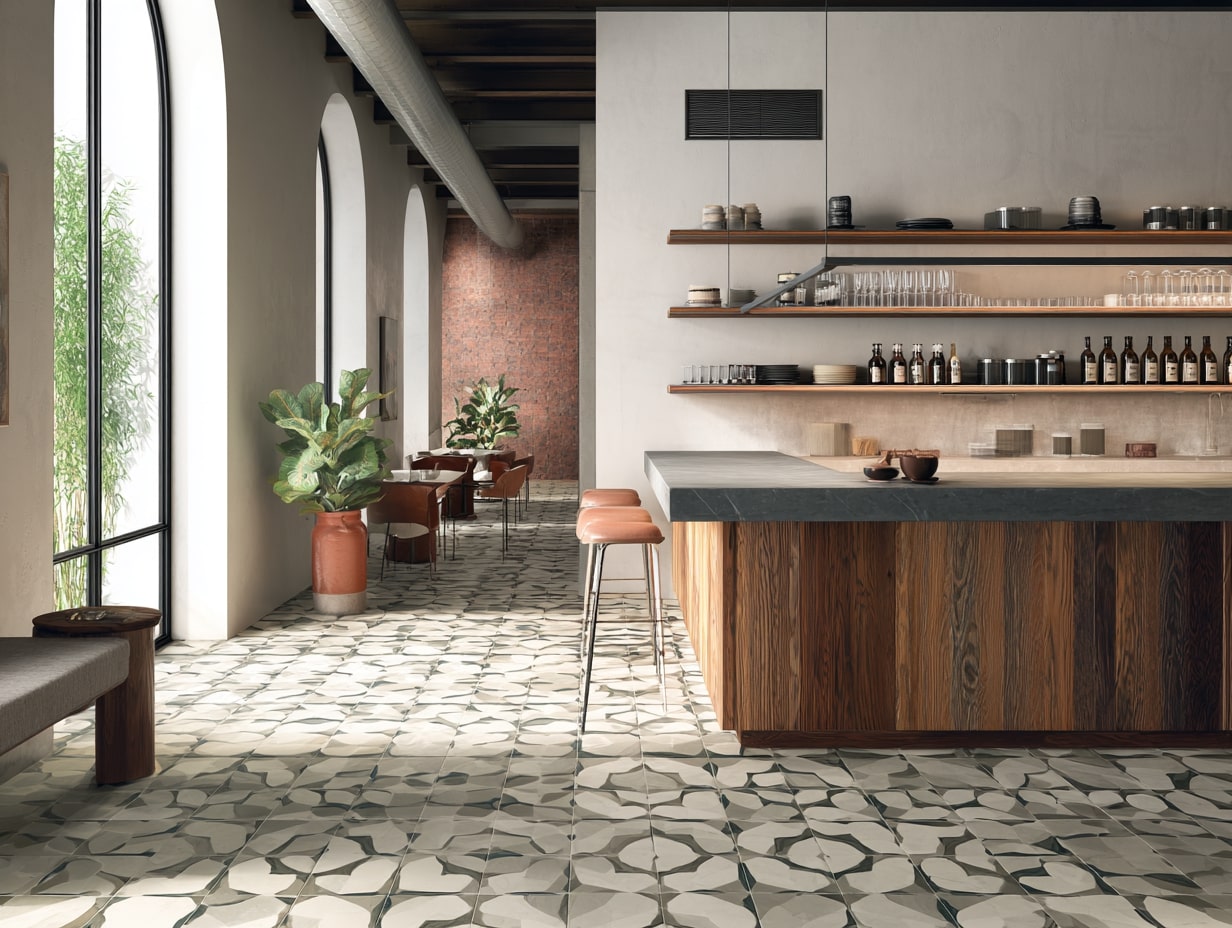

Natural Stone: Responsible Quarrying, Sealers, And Reuse Potential
Stone can last generations if we detail it right. We ask for quarry stewardship documentation and regional sourcing to cut transport impacts. Breathable, low-VOC sealers help maintenance. At remodels, we design for salvage, stone is ideal for reuse or recutting.
Bio-Based Resilient Surfaces: Linoleum And Emerging Bio-Resins
Linoleum: Plant-Based, Antimicrobial Properties, And Commercial Durability
True linoleum blends linseed oil, wood flour, cork, and jute backing. It’s naturally bacteriostatic, color-through, and repairable with heat and finish renewal. We specify welded seams in healthcare and use factory finish systems to streamline maintenance.
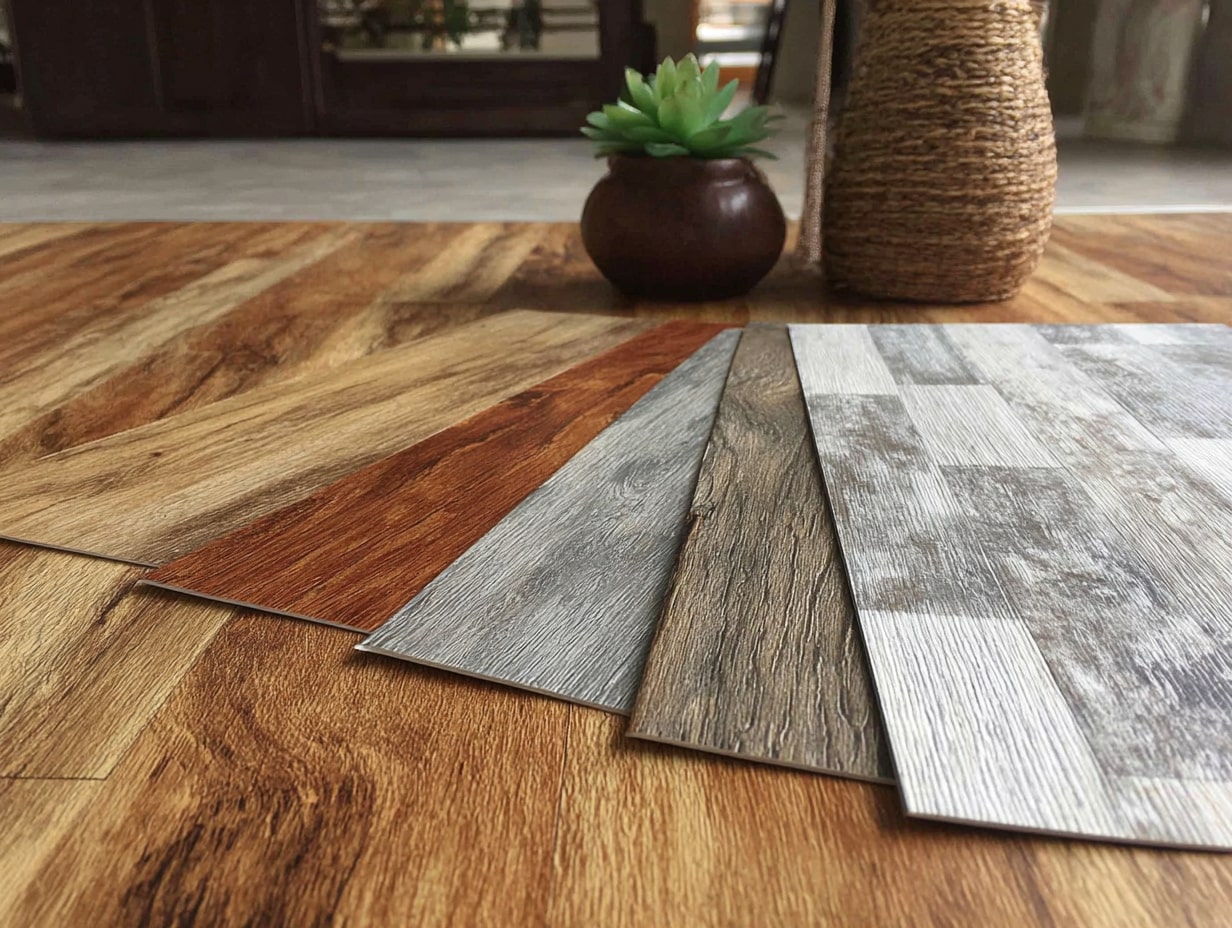

Bio-Based Solid Surfaces: Resin Innovations And Performance Trade-Offs
Next-gen resins derived from plants reduce fossil inputs while maintaining hardness and stain resistance. Still, heat tolerance and UV stability can vary. We review HPDs closely, confirm food-contact safety, and test samples for scratch/cleanability before committing.
Frontier Materials: Mycelium, Hemp-Lime, And Bio-Ceramics
Mycelium boards and acoustic panels are promising for interiors, with compostable cores. Hemp-lime shines as a wall system but is emerging for panels. Bio-ceramics offer low-temperature processing. For now, we use them in feature walls and low-wear elements to prove performance.
Specifying For Performance, Budget, And End Of Life
Application Matchups: Wet Areas, High-Traffic Floors, And Food-Contact Surfaces
Wet areas: porcelain, sintered stone, modified wood, or dense terrazzo with slip resistance. High traffic: terrazzo, porcelain, strand-woven bamboo, or linoleum with proper maintenance. Food-contact: sintered stone, select natural stones, paper composites verified food-safe.

Cost, Lead Times, And Local Sourcing To Reduce Impact
We balance first cost with total cost of ownership. Local or regional materials cut transport emissions and often lead times. Request lead-time forecasts early, and keep alternates pre-approved to avoid last-minute substitutions with higher environmental footprints.
Designing For Disassembly, Reuse, And Take-Back Programs
We design assemblies with mechanical fasteners, reversible sealants, and modular sizing. Ask vendors about take-back or buyback programs for tiles, metals, and carpets. Label materials and keep O&M manuals updated so future teams can repair, reclaim, or recycle.
Conclusion
Specifying top sustainable surface materials is about rigor plus restraint: choose verified low-impact products, detail them for longevity, and plan their next life. When we align performance, health, and circularity, our projects age gracefully, and our specs do too.
- biodegradable countertops
- carbon-neutral surface materials
- eco-conscious interior design
- eco-friendly surface design
- eco-materials for designers
- environmentally friendly surfaces
- green building materials
- green interior materials
- low-impact interior materials
- natural surface materials
- non-toxic surface materials
- reclaimed wood surfaces
- recycled surface materials
- renewable surface materials
- responsible design materials
- sustainable decor ideas
- sustainable design materials
- sustainable flooring options
- sustainable home design
- sustainable surface materials
Submit your architectural projects
Follow these steps for submission your project. Submission FormLatest Posts
Nature-Inspired Innovation: Biomimicry in Architecture
Biomimicry in architecture: a practical guide to nature-inspired design delivering 30–60% energy...
Green Architecture Explained: Designing for a Resilient Tomorrow
Green architecture explained through resilience: practical ways to cut carbon, improve health,...
Eco-Friendly Floor Coverings: Smart Choices for a Greener Home
Eco-friendly floor coverings made simple: discover sustainable materials, trusted certifications, and room-by-room...
What are Biodomes?
Biodomes are transforming architecture by blending ecological science with advanced design to...











Leave a comment