- Home
- Articles
- Architectural Portfolio
- Architectral Presentation
- Inspirational Stories
- Architecture News
- Visualization
- BIM Industry
- Facade Design
- Parametric Design
- Career
- Landscape Architecture
- Construction
- Artificial Intelligence
- Sketching
- Design Softwares
- Diagrams
- Writing
- Architectural Tips
- Sustainability
- Courses
- Concept
- Technology
- History & Heritage
- Future of Architecture
- Guides & How-To
- Art & Culture
- Projects
- Interior Design
- Competitions
- Jobs
- Store
- Tools
- More
- Home
- Articles
- Architectural Portfolio
- Architectral Presentation
- Inspirational Stories
- Architecture News
- Visualization
- BIM Industry
- Facade Design
- Parametric Design
- Career
- Landscape Architecture
- Construction
- Artificial Intelligence
- Sketching
- Design Softwares
- Diagrams
- Writing
- Architectural Tips
- Sustainability
- Courses
- Concept
- Technology
- History & Heritage
- Future of Architecture
- Guides & How-To
- Art & Culture
- Projects
- Interior Design
- Competitions
- Jobs
- Store
- Tools
- More
The Role of BIM Technology in Modern Architecture: Driving Efficiency and Innovation
Explore how BIM technology is revolutionizing modern architecture and construction by enhancing collaboration, precision, and sustainability. Learn about its transformative features, benefits like cost savings and visualization, challenges in implementation, and future advancements such as AI, cloud computing, and XR.

Table of Contents Show
In the world of modern architecture, innovation is shaping how we design, plan, and build. One game-changing advancement is Building Information Modeling (BIM) technology. It’s not just a tool; it’s a transformative process that’s redefining collaboration and efficiency in the construction industry. As architects and designers, we’re witnessing how BIM streamlines workflows and brings ideas to life with precision.
BIM allows us to create detailed, data-rich models that go beyond traditional blueprints. It’s revolutionizing how we visualize projects, predict challenges, and optimize resources. By integrating every aspect of a building’s lifecycle, from design to demolition, BIM is helping us build smarter, faster, and more sustainably.
As architecture evolves, the role of BIM continues to expand. It’s not just about keeping up with trends—it’s about pushing boundaries and reimagining what’s possible in the built environment. Let’s explore how this technology is shaping the future of design.
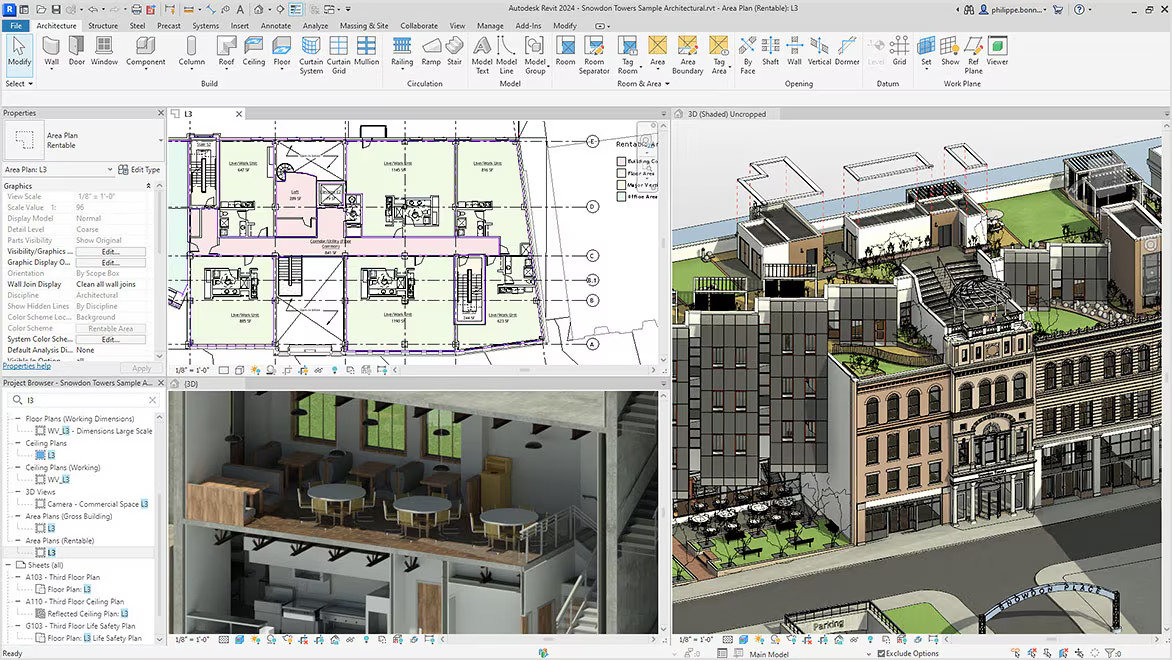
Understanding BIM Technology
Building Information Modeling (BIM) represents a transformative approach in architectural design and construction. By integrating data-driven processes, BIM facilitates precision, collaboration, and innovation.
What Is BIM?
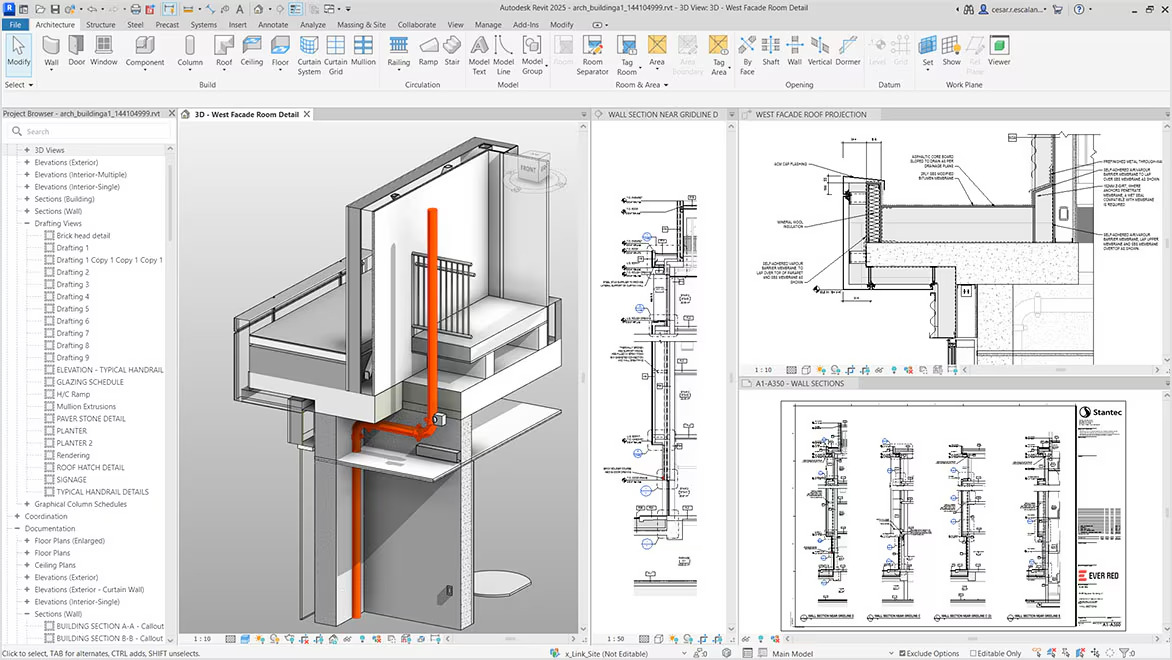
BIM refers to a process utilizing intelligent 3D models to inform and streamline the planning, design, construction, and operation of structures. It merges geometry, spatial relationships, and extensive data, creating a centralized model accessible to all project stakeholders. This ensures real-time updates and minimizes errors during the project lifecycle.
Key Features of BIM in Architecture
- 3D Visualization: BIM enables the creation of detailed 3D models, allowing teams to visualize designs before construction starts. For example, architects and engineers use it to identify aesthetic and functional adjustments early.
- Data Integration: BIM embeds critical data, such as material specifications, cost estimates, and structural details, into models. This integration accelerates decision-making and streamlines workflows.
- Clash Detection: By simulating construction sequences, BIM identifies conflicts between structural, mechanical, and electrical systems, reducing costly on-site rework.
- Lifecycle Management: BIM supports every stage of a building’s lifecycle, from design and construction to maintenance and eventual demolition. Facilities managers, for instance, use it for efficient asset management.
- Collaboration Capabilities: Cloud-based BIM platforms allow architects, engineers, and contractors to collaborate in real time. Stakeholders can review changes simultaneously, enhancing communication and reducing delays.
BIM’s role in architecture continues to expand, setting a new standard for efficiency and precision.
The Impact of BIM on Modern Architecture
Building Information Modeling (BIM) plays a pivotal role in shaping modern architecture by transforming the way architects, engineers, and stakeholders approach projects. Its comprehensive capabilities influence collaboration, design efficiency, and project accuracy, creating new opportunities for innovation.

Enhancing Collaboration and Communication
BIM facilitates seamless collaboration by integrating project data into a centralized model accessible to all stakeholders. Through tools like cloud-based platforms, we can share updates in real time, ensuring all team members remain aligned. For example, architects, engineers, and contractors can review conflicts, assess progress, and make informed decisions without delays. This fosters stronger communication and reduces the risk of misunderstandings.
Streamlining Design and Construction Processes
Using BIM improves efficiency in design and construction by automating repetitive tasks and optimizing workflows. We can generate 2D and 3D models simultaneously, identify clashes early, and simulate construction phases before physical work begins. For instance, setting up schedules and resource allocations within the BIM model allows for precise planning, minimizing project delays and budget overruns.
Improving Accuracy and Reducing Errors
BIM enhances accuracy by providing data-rich, digitally detailed models that eliminate inconsistencies. By detecting design and construction errors during the planning stage, we can significantly reduce costly modifications during execution. Clash detection tools, for example, identify overlaps in structural and mechanical elements, allowing us to address potential issues before construction starts. This rigorous validation process ensures higher-quality outcomes.
Advantages of BIM in Modern Architecture
BIM technology offers significant benefits in modern architecture. Its advantages span sustainability, cost and time savings, and enhanced design visualization.

Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
BIM integrates sustainability into design processes, enabling energy-efficient architecture. By simulating building performance during the early stages, we identify energy consumption patterns and optimize layouts for reduced environmental impact. Tools like daylight analysis and thermal simulations provide actionable data, improving energy efficiency in compliance with green building standards.
Cost and Time Efficiency
BIM minimizes costs and accelerates timelines through improved planning and precision. By automating quantities and cost estimates, we reduce budgeting errors and resource wastage. Clash detection ensures design conflicts are resolved before construction, lowering rework expenses. Coordinating schedules across multiple teams also enhances efficiency, allowing faster project delivery.
Better Visualization and Design Concepts
BIM improves design clarity through advanced visualization features. With accurate 3D models, we present lifelike representations to clients, enabling better decision-making. Virtual walkthroughs, combined with dynamic simulations, enhance design comprehension. These tools support creative and functional architectural concepts, aligning with client expectations while reducing design misinterpretations.
Challenges in Implementing BIM
Implementing Building Information Modeling (BIM) in modern architecture involves overcoming several obstacles. These challenges often arise due to technological, skill-based, and procedural constraints.

Technological Barriers
The adoption of BIM requires advanced hardware, software, and IT infrastructure. High-performance computers capable of handling large data sets and complex 3D models are essential. Limited compatibility between different BIM platforms, along with frequent software updates, can complicate collaboration. Additionally, ensuring data security in cloud-based BIM environments remains a concern.
Training and Skill Development
Teams must possess comprehensive knowledge of BIM tools and methodologies to maximize their benefits. Training programs and resources need to address the varying proficiency levels among professionals. A lack of skilled staff can delay adoption and reduce the potential efficiencies BIM offers.
Integration With Traditional Methods
Shifting from traditional practices to BIM workflows can be disruptive. Existing teams and stakeholders accustomed to 2D design methods may resist adopting new processes. Misalignment between BIM’s collaborative model and conventional project delivery frameworks can hinder seamless implementation. Proper transition strategies are crucial to mitigate resistance and encourage adoption.
The Future of BIM Technology in Architecture
BIM technology continues to evolve, redefining industry standards and opening new possibilities for innovation and efficiency. Emerging advancements and potential trends are set to shape the future of architecture.

Innovations and Advancements
Advancements in BIM are driving integration with cutting-edge technologies, amplifying its capabilities. For instance, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) enhance BIM workflows by automating complex tasks like pattern recognition, material selection, and predictive analytics. Generative design tools in BIM platforms support architects in exploring countless design permutations quickly, optimizing outcomes based on specified goals.
Cloud-based BIM platforms are improving collaboration by enabling real-time updates and remote access. Data sharing across global teams encourages seamless communication and ensures project alignment. Integration with IoT devices enhances building monitoring during operations, connecting BIM environments directly to building management systems for real-time performance data.
Extended reality (XR), including virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR), enriches 3D visualization by creating immersive design reviews and client presentations. With XR, stakeholders interact with spatial layouts and make informed decisions during pre-construction stages, minimizing revisions and boosting project precision.
Potential Industry Trends
Sustainability remains central to future BIM adoption. BIM’s capacity to simulate energy performance and environmental impacts encourages green building practices. As regulatory frameworks for sustainable construction strengthen, integrating LEED and net-zero standards into BIM workflows becomes vital.
A growing focus on modular construction aligns closely with BIM’s strengths. By integrating prefabrication and BIM models, we streamline processes like assembly planning and optimize logistics to reduce waste and improve timeline predictability.
Open BIM standards are gaining traction to address interoperability challenges. These standards allow smoother data exchange between platforms, fostering broader collaboration among architects, engineers, and contractors. This shift highlights the industry’s commitment to reducing inefficiencies caused by proprietary software limitations.
The integration of blockchain technology in BIM processes is gaining attention for its potential in enhancing data security and transparency. Blockchain can ensure the integrity of digital models by preventing unauthorized alterations and creating an immutable record of changes throughout the project lifecycle.
Conclusion
BIM technology is redefining modern architecture by driving efficiency, precision, and innovation. Its ability to integrate data-rich models into every stage of a building’s lifecycle transforms traditional workflows. With features like 3D visualization, clash detection, and centralized data access, BIM promotes better collaboration and reduces errors, ensuring higher-quality outcomes.
Key advantages, such as sustainability integration, cost efficiency, and enhanced visualization, make BIM essential for addressing modern architectural demands. By optimizing energy usage and resource allocation, BIM supports eco-friendly design practices. Its automation capabilities simplify complex tasks, saving both time and expenses while providing detailed 3D models that improve decision-making and client satisfaction.
Despite its benefits, implementing BIM poses challenges like the requirement for advanced equipment, platform compatibility issues, and the need for specialized skills. Overcoming these hurdles requires strategic planning and team training, easing the transition from traditional methods to BIM-centered processes.
As advancements like AI, ML, cloud computing, and XR technologies enhance BIM’s potential, the industry moves toward more sustainable, transparent, and collaborative practices. Emerging trends, including blockchain and open standards, further reinforce BIM’s role in shaping the future of architecture. By addressing its challenges and leveraging its capabilities, we can realize the full impact of BIM on modern design and construction.
- architectural innovation with BIM
- architecture design using BIM
- BIM and construction management
- BIM and modern building design
- BIM benefits in architecture
- BIM driving efficiency
- BIM for sustainable architecture
- BIM implementation in construction
- BIM software for architecture
- BIM solutions for architects
- BIM technology advancements
- BIM technology in architecture
- BIM technology trends
- BIM tools for architects
- Building Information Modeling
- construction efficiency with BIM
- enhancing architecture with BIM
- innovative architecture with BIM
- modern architecture BIM
- smart architecture with BIM
Submit your architectural projects
Follow these steps for submission your project. Submission FormLatest Posts
Becoming a BIM Expert: How BIM Is Transforming Architectural Practice
Building Information Modeling is no longer just a technical requirement in architectural...
BIM in Architecture: What You Need to Know for Smarter Building Design
Discover how Building Information Modeling (BIM) is transforming architecture with intelligent 3D...
The Future of Architecture: How the BIM Industry Is Changing Design and Construction
Explore how Building Information Modeling (BIM) is revolutionizing architecture with enhanced collaboration,...
How the BIM Industry is Transforming Modern Construction Practices for a Better Future
Discover how Building Information Modeling (BIM) is revolutionizing the construction industry by...












Leave a comment