- Home
- Articles
- Architectural Portfolio
- Architectral Presentation
- Inspirational Stories
- Architecture News
- Visualization
- BIM Industry
- Facade Design
- Parametric Design
- Career
- Landscape Architecture
- Construction
- Artificial Intelligence
- Sketching
- Design Softwares
- Diagrams
- Writing
- Architectural Tips
- Sustainability
- Courses
- Concept
- Technology
- History & Heritage
- Future of Architecture
- Guides & How-To
- Art & Culture
- Projects
- Interior Design
- Competitions
- Jobs
- Store
- Tools
- More
- Home
- Articles
- Architectural Portfolio
- Architectral Presentation
- Inspirational Stories
- Architecture News
- Visualization
- BIM Industry
- Facade Design
- Parametric Design
- Career
- Landscape Architecture
- Construction
- Artificial Intelligence
- Sketching
- Design Softwares
- Diagrams
- Writing
- Architectural Tips
- Sustainability
- Courses
- Concept
- Technology
- History & Heritage
- Future of Architecture
- Guides & How-To
- Art & Culture
- Projects
- Interior Design
- Competitions
- Jobs
- Store
- Tools
- More
Sustainable 3D Printing with Clay: Revolutionizing Architecture Construction Material
Discover how 3D printing is revolutionizing architecture by combining the timeless advantages of clay with modern technology. Learn about eco-friendly benefits, intricate designs, cost savings, and sustainable solutions in construction. Explore cutting-edge techniques and innovations shaping the future of clay-based structures.
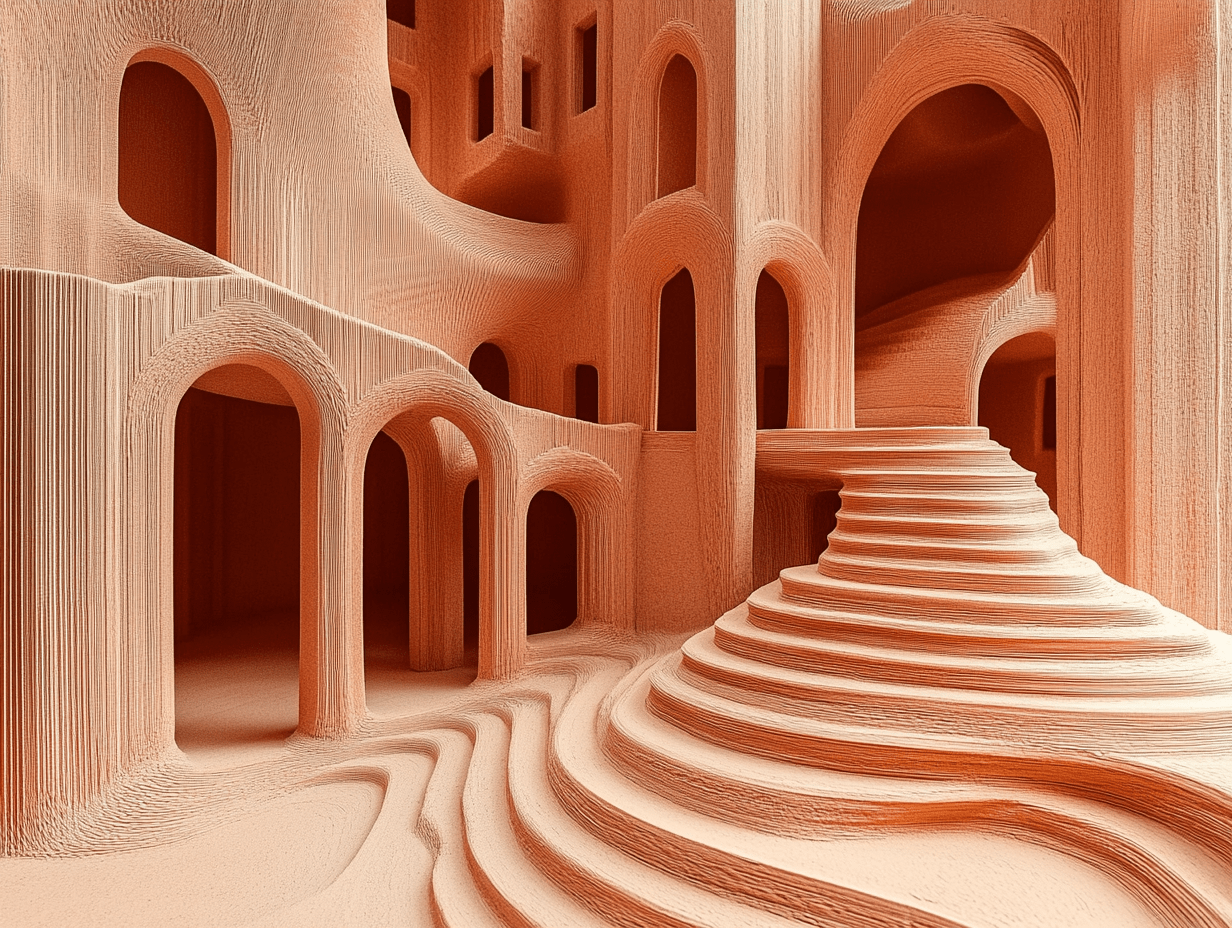
Table of Contents Show
3D printing is revolutionizing how we approach construction, and clay, one of the oldest building materials, is finding new life in this cutting-edge technology. By combining tradition with innovation, we’re unlocking possibilities that could reshape sustainable architecture and redefine how we build. It’s fascinating to see how something so ancient can seamlessly integrate with modern advancements.
As we explore 3D-printed clay in construction, we’re not just looking at unique designs but also at eco-friendly solutions that reduce waste and energy use. This method offers a promising alternative to conventional materials, making it a game-changer for architects and builders alike. The potential for creating durable, sustainable, and aesthetically stunning structures has never been more exciting.

Overview Of 3D Printing In Construction
3D printing in construction transforms how structures are designed and built. By layering materials using precise digital models, this technology reduces labor costs, material waste, and environmental impact compared to traditional methods. Its growing adoption demonstrates its potential to redefine the industry.
Additive manufacturing methods play a critical role in creating complex geometries. Unlike conventional techniques, 3D printing enables the construction of intricate architectural forms with minimal material usage. This ability meets both aesthetic and functional needs while enhancing efficiency.
Material diversity broadens the scope of 3D printing applications. Builders use materials like concrete, polymers, and now clay to address different structural requirements and environmental considerations. Clay, in particular, offers sustainability advantages due to its natural origin and low-carbon profile.
Scalability distinguishes 3D printing from other construction methods. From small-scale residential projects to large public structures, this innovation supports faster, cost-effective solutions while maintaining high accuracy and durability standards.
The Role Of Clay As A Construction Material
Clay serves as a versatile and sustainable option in construction. Its adaptability makes it ideal for use in modern techniques such as 3D printing while maintaining eco-friendly benefits.
Benefits Of Using Clay In Architecture
- Sustainability
Clay, being naturally abundant and biodegradable, reduces environmental degradation. Unlike synthetic materials, it decomposes without leaving toxic residue.
- Thermal Efficiency
Structures made from clay provide excellent insulation. This reduces energy use for heating or cooling in different climates.
- Cost-Effectiveness
Extracting and processing clay locally lowers material transport costs. Combined with 3D printing, it minimizes waste and maximizes efficiency.
- Aesthetic Versatility
Clay offers a range of textures, colors, and finishes. Its malleability enables complex designs, enhancing architectural creativity.
- Durability
Properly treated clay resists weathering, ensuring longevity in various environmental conditions.
- Structural Limitations
Clay’s natural properties may limit its load-bearing capacity. Strength reinforcement or blending with other materials becomes necessary for large-scale projects.
- Moisture Sensitivity
Unsealed clay absorbs water, leading to potential degradation. Protective coatings are essential for maintaining structural integrity.
- Processing Time
Drying and curing clay can extend overall construction timelines, particularly in humid conditions.
- Skill Requirements
Mastery in handling clay, especially for 3D-printing applications, is vital to avoid defects or inconsistencies in structures.
- Local Variability
Clay quality and availability differ by region, requiring material testing and adaptation to local conditions.
By addressing these challenges, we can maximize clay’s potential as a sustainable and functional construction material through advanced 3D printing technologies.

3D Printing Techniques For Clay Architecture
3D printing introduces precision and versatility to clay-based construction. Advanced techniques enable the creation of sustainable structures with optimized designs and material usage.
Types Of 3D Printing Technologies Used
Different technologies target varied architectural requirements, enhancing efficiency and design flexibility.
- Binder Jetting: This method uses a liquid binding agent to solidify layers of clay powder. It’s suitable for intricate shapes and detailed structures due to its high precision.
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): FDM extrudes clay through a nozzle, allowing controlled layering. It is ideal for functional prototypes and small-scale architectural elements.
- Robotic Arm Extrusion: Using flexible robotic arms to deposit clay enables the construction of large-scale structures with complex geometries. This technology is commonly applied in direct construction projects.
Innovations In Clay Printing Methods
Innovative methods redefine the use of clay in architectural 3D printing, optimizing both performance and aesthetics.
- Adaptive Layering Techniques: Advanced software adjusts the layer thickness based on structural needs, reducing material waste while maintaining integrity.
- Multi-Material Integration: Combining clay with other materials enhances strength or adds insulation, addressing specific architectural challenges.
- Eco-Optimized Clay Mixtures: Modified clay compositions reduce drying time and improve load-bearing capacity while retaining ecological benefits.
- Parametric Design Integration: Digital modeling tools allow for intricate, nature-inspired designs that maximize efficiency and visual appeal.

Advantages Of 3D Printed Clay Structures
3D printed clay structures combine traditional clay’s eco-friendly properties with modern technological precision. This approach enhances sustainability, cost-effectiveness, and design versatility in architecture.
Sustainability And Environmental Impact
3D printed clay structures offer significant environmental benefits due to the material’s natural abundance and the efficiency of additive manufacturing. Clay is biodegradable and locally sourced, reducing transportation emissions and dependency on synthetic materials. The precise layering process minimizes material waste, as only the required amount of clay is used. Compared to traditional construction methods, 3D printing consumes less energy, resulting in a lower carbon footprint. For instance, integrating eco-optimized clay mixtures further enhances energy efficiency by maintaining thermal insulation properties and reducing heating or cooling demands. These aspects position 3D printed clay as a sustainable alternative in architecture.
Cost-Effectiveness And Efficiency
Cost advantages stem from reduced material waste, lower labor needs, and the accessibility of clay as a raw material. The automation involved in 3D printing reduces the reliance on skilled manual labor, which is typically expensive. Clay’s natural availability decreases raw material expenses compared to imported or synthetic options. Additionally, the construction timeline is significantly shortened using 3D printing techniques, cutting labor and overhead costs. For example, robotic arm extrusion enables continuous and precise clay deposition, reducing production inefficiencies while maintaining structural integrity. These factors ensure efficient resource utilization and cost savings without compromising quality.
Challenges And Limitations
Despite the potential of 3D-printed clay in construction, several challenges and limitations affect its widespread adoption. Addressing these issues is essential to fully realize its benefits in architecture.
Technical Barriers
The technical complexity of 3D printing clay poses significant challenges. Clay’s consistency requires precise calibration during the extrusion process, as variations can lead to nozzle blockages or deformation in printed structures. Maintaining uniform moisture content is also critical since inconsistency can cause cracking or surface imperfections. Developing optimized clay mixtures for specific applications demands extensive research, which limits scalability.
The reliance on advanced equipment and software integration increases operational complexity. Robust 3D printers capable of handling heavy clay material are costly, and dependency on highly specialized skill sets for operation further restricts accessibility. Real-time monitoring systems are necessary to ensure quality and stability, complicating implementation in large-scale projects.
Durability Concerns
Clay’s inherent properties impact the durability of 3D-printed structures. Its sensitivity to moisture remains a significant limitation. Without proper treatment or protective coatings, excessive humidity can weaken or degrade structures over time. Seasonal changes in temperature further exacerbate wear due to thermal expansion or contraction.
Load-bearing capacity also presents concerns, as 3D-printed clay structures often struggle to match the strength of traditional concrete for larger, more demanding architectural projects. While additives can improve performance, the compatibility of these materials with sustainable practices introduces additional constraints. Addressing these durability issues is essential to extend the lifespan of clay-based architectural applications.

Future Of 3D Printing Clay Architecture
The future of 3D printing clay architecture is shaping up to be innovative and transformative, with advancements promising to redefine construction practices. Emerging trends and potential applications are expanding its role in modern architecture.
Emerging Trends In The Industry
Several trends are pushing the boundaries of 3D printing clay architecture. Enhanced automation through AI-driven systems is improving precision and reliability during material deposition. These systems allow for real-time adjustments, minimizing errors while increasing structural consistency.
Multi-material 3D printing is gaining traction, enabling the integration of clay with other sustainable materials like fibers or biopolymers for improved structural performance. This approach enhances durability and broadens the range of design possibilities.
Advancements in robotics, such as mobile and autonomous robotic arms, are further expanding the scalability of clay-based 3D printing. These systems support larger projects and more intricate designs, making them adaptable to diverse construction needs. Innovations in eco-compatible clay formulations are also emerging, using locally sourced or recycled components to reduce environmental impact.
Potential Applications In Modern Architecture
3D-printed clay architecture holds vast potential across various applications. In residential housing, it’s paving the way for affordable and sustainable home construction, especially in regions with resource constraints. The use of abundant local clay ensures cost-effectiveness without sacrificing quality.
In public infrastructure, clay-based 3D printing is making it possible to create eco-friendly community spaces, such as pavilions, cultural centers, or small bridges. Its adaptability to parametric designs makes it ideal for unique and aesthetically appealing public structures.
For heritage restoration projects, 3D printing clay offers precision in recreating damaged architectural details while maintaining the authenticity of historical designs. By mirroring traditional clay craftsmanship, it preserves cultural heritage while leveraging modern efficiency. Temporary event structures, such as exhibition spaces or art installations, are also gaining from its rapid production and customizability.
Overall, these applications demonstrate how 3D printing clay can address both functional and creative architectural challenges.
Conclusion
3D printing with clay transforms architecture by combining traditional materials with modern precision. This technique enhances sustainability, reduces waste, and enables intricate designs. It addresses critical challenges in the construction industry while unlocking opportunities for eco-friendly and efficient building practices.
Emerging technologies like AI-driven automation, multi-material integration, and robotics improve scalability and performance. These developments, paired with optimized clay mixtures, reduce environmental impact and refine construction applications. Potential uses include affordable housing, heritage restoration, eco-friendly infrastructure, and event-specific structures, offering practical and creative solutions for contemporary architecture.
By overcoming technical and material limitations, 3D printing clay advances sustainable construction. It broadens design possibilities while maintaining cost-effectiveness and environmental responsibility. These innovations redefine architectural practices, fostering a future where creativity and sustainability align.
- 3D printed clay architecture
- 3D printed structures
- 3D printing for architects
- 3D Printing in Construction
- advanced construction technology
- carbon footprint reduction in construction
- clay 3D printing
- clay building materials
- eco-friendly construction materials
- environmentally friendly construction
- green building technology
- Innovative construction materials
- revolutionary architecture material
- Sustainable 3D printing
- sustainable architecture solutions
- sustainable building practices
Submit your architectural projects
Follow these steps for submission your project. Submission FormLatest Posts
Self-Sufficient 3D-Printed House: WASP’s Itaca Model
WASP's Itaca project in Northern Italy is the first certified self-sufficient 3D-printed...
9 Best Timber Frame Home Builders In PA For Sustainable Building And Design
Table of Contents Show Why timber frame construction makes sense in PennsylvaniaBudgeting...
How Upcycling Materials Is Redefining the Future of Architectural Construction
Upcycling materials is reshaping how architecture understands value, time, and responsibility. Rather...
Architecture Trends 2024: Top 10 Design Ideas Shaping Spaces
Architecture trends 2024 are redefining how we design and experience spaces. From...












Leave a comment