- Home
- Articles
- Architectural Portfolio
- Architectral Presentation
- Inspirational Stories
- Architecture News
- Visualization
- BIM Industry
- Facade Design
- Parametric Design
- Career
- Landscape Architecture
- Construction
- Artificial Intelligence
- Sketching
- Design Softwares
- Diagrams
- Writing
- Architectural Tips
- Sustainability
- Courses
- Concept
- Technology
- History & Heritage
- Future of Architecture
- Guides & How-To
- Art & Culture
- Projects
- Interior Design
- Competitions
- Jobs
- Store
- Tools
- More
- Home
- Articles
- Architectural Portfolio
- Architectral Presentation
- Inspirational Stories
- Architecture News
- Visualization
- BIM Industry
- Facade Design
- Parametric Design
- Career
- Landscape Architecture
- Construction
- Artificial Intelligence
- Sketching
- Design Softwares
- Diagrams
- Writing
- Architectural Tips
- Sustainability
- Courses
- Concept
- Technology
- History & Heritage
- Future of Architecture
- Guides & How-To
- Art & Culture
- Projects
- Interior Design
- Competitions
- Jobs
- Store
- Tools
- More
Understanding Architectural Structural Diagrams: Evolution and Impact
A structural diagram in architecture maps out every load path, connection, and material choice that keeps a building standing. This guide covers the key components of architectural structural diagrams—from load-bearing elements and material specifications to connection details and standardized symbols—plus different diagram types, creation best practices, and the evolution from hand drafting to BIM and AI-powered workflows.

Table of Contents Show
- What Is a Structural Diagram in Architecture?
- Key Components: How to Identify the Structures on the Diagram
- The Importance of Structural Diagrams in Architecture
- Different Types of Architectural Structural Diagrams
- Creating an Architectural Structural Diagram
- The Evolution of Structural Diagrams: From Hand Drafting to Digital Modeling
- Structural Diagram Architecture: Best Practices for Professionals
A structural diagram in architecture serves as the blueprint of a building’s strength, mapping out every load path, connection, and material choice that keeps a structure standing. These architectural diagrams are the backbone of any construction project, guiding engineers and architects through the complex dance of physics and aesthetics that bring buildings to life. From the towering skyscrapers that define our city skylines to the homes that cradle our families, every architecture structure diagram begins with this crucial plan.
Understanding an architectural structural diagram is essential for anyone involved in the building process. These diagrams detail the skeleton of a structure, showing how various elements like beams, columns, and walls interact to support the building. They take into account the myriad forces a building must withstand, from the weight of its own materials to environmental challenges like wind and seismic activity. It’s a fascinating intersection of art and science, where every line and symbol on the page translates to the physical components that ensure a building’s durability and safety. Whether you are an architecture student or a seasoned professional, learning to identify the structures on the diagram is a fundamental skill in structural architecture.
Our journey through the world of architectural structural diagrams reveals the meticulous planning and calculation that underpin our built environment – the kind of work that often relies on tools like a moment of inertia calculator. It’s a testament to human ingenuity and the relentless pursuit of innovation, standing on the shoulders of historical marvels like the Eiffel Tower and the Brooklyn Bridge. Join us as we delve into the foundations of architecture, exploring how these structure diagrams shape the spaces we inhabit and the landmarks we admire.

What Is a Structural Diagram in Architecture?
The Basic Concept and Purpose
So, what is a diagram in architecture that focuses on structure? Architectural structural diagrams are visual tools that exemplify the backbone of construction projects. These diagrams encapsulate the essence of a building’s framework by displaying the interaction and alignment of various structural elements such as beams, columns, walls, and foundations. Their primary purpose is to ensure that every part of the building can withstand environmental pressures while maintaining structural integrity and safety. According to the American Institute of Architects (AIA), clear structural documentation is one of the pillars of professional architectural practice.
An architectural diagram focused on structure serves several key functions in the construction and design industry. Firstly, it provides a clear and comprehensive overview of a building’s structure, allowing engineers and architects to analyze and adjust the design as necessary. By documenting the spatial relationship between different components, these diagrams facilitate informed decision-making regarding materials, dimensions, and construction techniques. Modern BIM technology has significantly enhanced the accuracy and collaborative potential of these diagrams.
Moreover, these structure diagrams act as a communication bridge among all stakeholders involved in the construction project, including designers, engineers, contractors, and clients. They help in setting clear expectations, enabling a unified understanding of the project’s structural requirements. This, in turn, streamlines the construction process, reduces the risk of errors, and ensures that the project adheres to the highest quality standards.
In addition to their practical applications, architectural structural diagrams also play a critical role in preserving the artistic vision of a building. They balance aesthetic appeal with technical precision, ensuring that the final structure is not only safe and functional but also visually appealing. This intersection of art and engineering is what gives iconic structures, such as the Eiffel Tower and the Brooklyn Bridge, their lasting legacy.
In essence, a structural diagram architecture approach is indispensable in the realm of construction and architecture. These diagrams embody the meticulous planning and calculation that goes into creating safe, durable, and aesthetically pleasing structures. Through these diagrams, we gain insight into the invisible forces that shape our built environment, ensuring that the spaces we inhabit and admire stand the test of time.
Key Components: How to Identify the Structures on the Diagram
Understanding the key components of structural diagrams is imperative for both students and professionals in the architecture and engineering fields. When you learn to identify the structures on the diagram, you unlock the ability to read the visual language that communicates how a building stands, resists loads, and maintains its form. These diagrams not only detail the physical aspects of a structure but also communicate the thought process and considerations behind a building’s design and integrity. Let’s delve into the crucial aspects that make up structural diagrams used by architects.

Load-Bearing Elements and Form
A foundational aspect of structure diagram architecture, load-bearing elements include beams, columns, walls, and footings. These components ensure the stability and safety of a building by supporting and distributing various loads, including gravity, wind, seismic, and live loads. The form, or shape, of these elements is equally important, as it directly influences the efficiency and overall aesthetic of a building. For instance, the innovative forms of historical marvels like the Eiffel Tower and the Brooklyn Bridge not only provide structural support but also contribute to their iconic status. In our designs, we meticulously plan the arrangement and scale of these elements to achieve a balance between functionality and visual appeal.
Material Specifications
Selecting the appropriate materials for the structural elements is crucial for ensuring durability, safety, and cost-effectiveness. Material specifications detail the type, quality, and strength of the materials used, ranging from various grades of concrete and types of steel reinforcement to finishes. These specifications are integral in meeting design requirements and conforming to international building codes. For example, the choice of steel for the Brooklyn Bridge’s cables was pivotal in achieving the necessary tensile strength while maintaining the desired slim profile. In our projects, we thoroughly specify materials to ensure that every structure meets the desired standards of strength and aesthetics.
Connection Details
The details of how structural components are interconnected, or connection details, play a significant role in the integrity of a building. These details include information on welding, bolting, and the use of connectors to join beams to columns, walls to foundations, and so forth. Correct connection details are vital to ensure that the structure functions as a coherent system, capable of withstanding loads and stresses without failure. Drawing from historical examples, the precise connection methods employed in the construction of the Eiffel Tower were essential for distributing the tower’s weight and providing stability. In our work, we emphasize the importance of accurately detailing connection specifications in structural diagrams to guarantee both the safety and longevity of the structures we design.
Symbols and Notations in Structural Diagrams
Every architectural diagram relies on a standardized set of symbols and notations to convey technical information efficiently. Structural engineers and architects use specific line types, hatching patterns, and graphic symbols to represent different materials (such as concrete, steel, or timber), support conditions (fixed, pinned, or roller), and force directions. Understanding these symbols is the first step to accurately identify the structures on the diagram. Organizations like the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and national bodies publish guidelines that ensure diagrams are readable across different countries and practices.
By concentrating on these key components, we ensure that our structure diagrams not only serve as a blueprint for construction but also exemplify our commitment to creating structures that are both functional and aesthetically pleasing.
The Importance of Structural Diagrams in Architecture
From Concept to Construction
Structural diagrams play a pivotal role in the evolution of architectural design from its inception to the final construction phase. These diagrams provide a detailed representation of the structural elements of a building, including load paths, connections, and materials. By offering insight into the structural integrity of a design, they allow architects and engineers to assess the feasibility and ensure that the building can withstand various stresses and forces.
Moreover, structural diagrams are invaluable during the construction process. Contractors and construction teams rely on them to understand the specifications and details of the project. This ensures that the building is constructed accurately, adhering to the designed safety standards and aesthetic considerations. Furthermore, these diagrams help in identifying potential issues before construction begins, saving time and resources.
Structural diagrams are an important tool that helps architects, engineers, and contractors work together by creating a clear visual plan everyone can understand. This teamwork is especially important when dealing with complex load distributions or adding unique design features. Advanced graphing calculation tools have made these diagrams more accurate and easier to use. With these tools, professionals can map stress points, simulate how loads behave, and optimize materials to reduce waste. For a deeper dive into how architectural and structural coordination is managed digitally, explore how BIM software integrates structural data into a unified 3D model.

Communication Among Professionals
One of the most crucial aspects of architectural projects is the seamless communication among different professionals involved, including architects, engineers, contractors, and clients. Structural diagrams serve as a common language, facilitating clear and precise communication about the design intentions and structural details of the project.
These diagrams simplify complex architectural and structural concepts, making them accessible to non-specialists. Consequently, they enhance the decision-making process, allowing stakeholders to make informed choices about materials, construction methods, and design adjustments.
Additionally, structural diagrams contribute to efficient teamwork by ensuring that all team members have a unified understanding of the project. This coordinated approach not only streamlines the workflow but also helps in maintaining the integrity of the original design, ensuring that the final construction mirrors the envisioned architectural masterpiece. For more about how diagrams facilitate the architectural diagram design process, see our dedicated guide.
In essence, structural diagrams are indispensable tools in the architecture and construction industries. They bridge the gap from concept to construction, ensuring that structures are not only aesthetically pleasing but also strong, safe, and functional. Furthermore, they foster effective communication among professionals, laying the foundation for successful project completion.
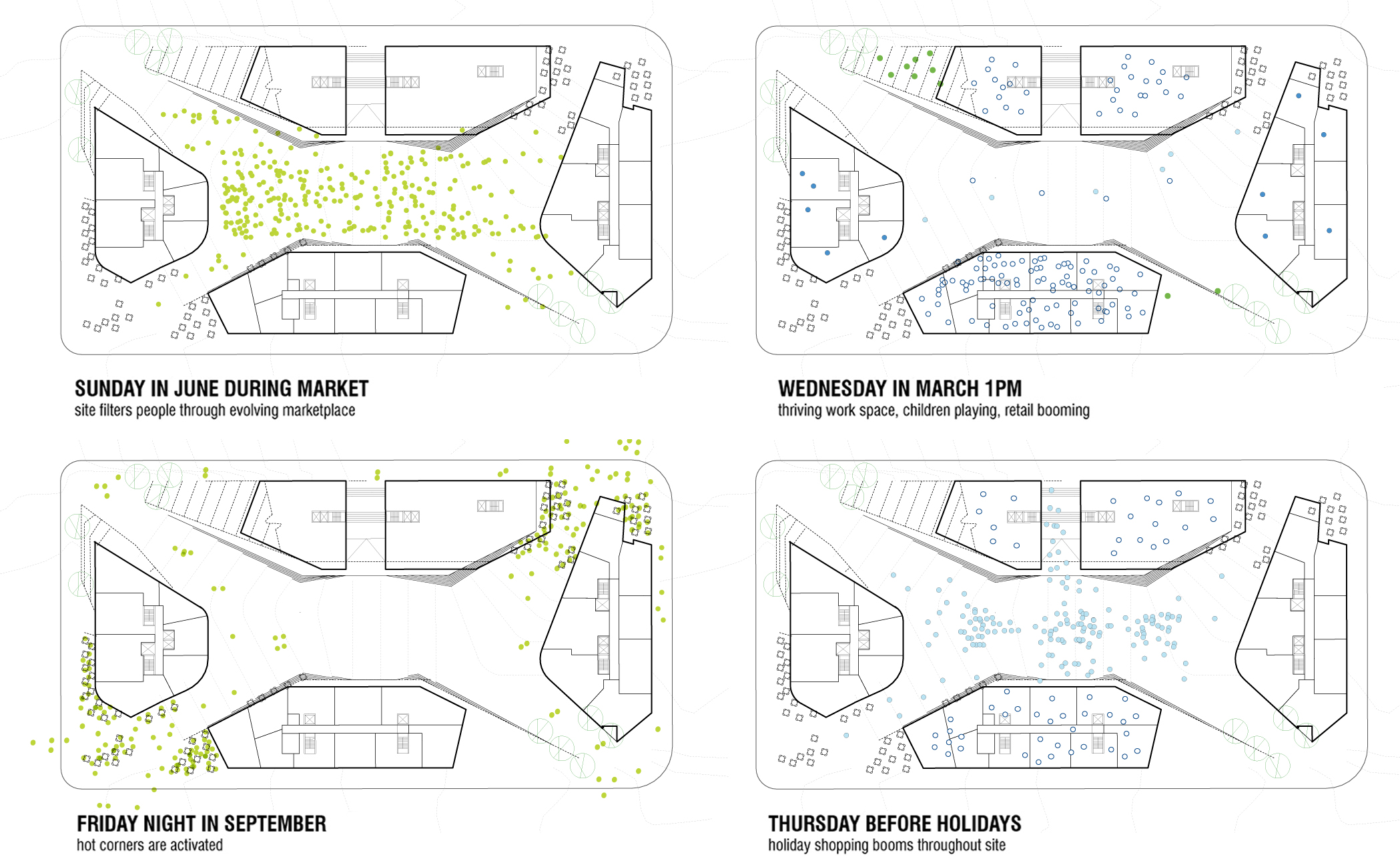
Different Types of Architectural Structural Diagrams
Foundation and Floor Plans
When we create architecture structure diagrams, detailed foundation and floor plans become crucial. These diagrams illuminate the various aspects of a building’s foundation, showcasing the depth, size, and type of foundations such as strip footings, isolated footings, or mat foundations. Our primary goal here is to ensure that the building’s base distributes the structure’s load evenly to the ground beneath, providing a solid foundation for safety and stability. Moreover, floor plans give an overview of the layout, detailing the arrangement of spaces and the location of structural elements. These plans are indispensable for a comprehensive understanding of the structural composition of a building from the ground up. You can also explore how programme and function diagrams complement structural floor plans by mapping spatial organization.
Frame and Roof Diagrams
Moving upwards, frame and roof diagrams offer a blueprint for constructing the skeleton of a building. These drawings play a pivotal role in depicting the layout and design of the structural framework, including floor and roof framing. Floor framing diagrams detail the arrangement of beams, joists, and floor supports, ensuring that each level of the building is adequately supported. Roof framing diagrams, on the other hand, outline the structure that supports the roof coverings, emphasizing the beams, rafters, and trusses designed to withstand environmental loads. Together, frame and roof diagrams ensure that the structural integrity of a building is maintained, safeguarding against potential failures.

Elevations and Sections
Elevations and sections provide unique perspectives that complement the foundational and framing plans. Elevations are essential for understanding the exterior aesthetics of a building, depicting the façade features, window and door placements, and overall height. These diagrams allow stakeholders to visualize the building in its environment, aiding in the identification of potential design conflicts. Sections, however, cut through the structure, offering a view of the interior. These diagrams detail the relationships between different levels, room sizes, and the integration of structural elements with mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems. Elevations and sections together supply a comprehensive view of the building’s appearance and internal workings, enhancing clarity and facilitating better communication among professionals involved in the construction process. For a broader perspective on drawing types, see our guide on general arrangement drawings in architecture.
Our expertise in producing various architectural structural diagrams ensures that every aspect of a building’s design is meticulously planned and communicated. From the foundation to the roof, and everything in between, we provide detailed insights into the structural integrity and aesthetic considerations of a building, fostering successful project completion.
Creating an Architectural Structural Diagram
Creating an architectural structural diagram is a critical part of the design process, enabling us to visualize and communicate the structural elements of a building project effectively. These diagrams serve as blueprints that detail the engineering behind a building’s design, covering everything from the foundation to the roof. In this section, we delve into three essential aspects: identifying structural requirements, ensuring clarity and precision in the diagrams, and the tools and techniques beneficial for drafting these critical documents.
Identifying Structural Requirements
The first step in creating a structural diagram is to identify the structural requirements of the building. This involves understanding the load-bearing capacities needed for the structure to remain safe and stable under various conditions. We examine elements like columns, beams, walls, and foundations, determining the types and quantities of materials required. Analyzing environmental factors such as wind, seismic activity, and soil conditions is crucial, as these will significantly impact the building’s structural design. By accurately identifying these requirements, we can ensure that the structure will withstand the tests of time and nature.
Considerations for Clarity and Precision
Once we’ve identified the structural requirements, our next focus is on ensuring that our diagrams are clear and precise. Clarity in an architectural structural diagram ensures that every stakeholder, from architects to builders, can understand the vision and technical necessities of the project. We achieve this by using standardized symbols and notations that communicate specific information unambiguously. Precision is equally important, as even minor inaccuracies can lead to significant issues during construction. We meticulously detail measurements, material strengths, and connection points to ensure that the structure can be built as designed, without room for error.

Tools and Techniques for Drafting
In drafting architectural structural diagrams, we rely on a combination of traditional and modern tools and techniques. Hand-drawn sketches often serve as the initial step, allowing for rapid visualization of ideas and structural concepts. However, digital tools and software like AutoCAD and Revit have become indispensable in our workflow. These programs support us in creating detailed, accurate diagrams capable of being shared and edited collaboratively. Digital drafting not only streamlines the design process but also enhances precision, with features that automatically calculate loads, dimensions, and materials. The integration of AI and BIM with advanced simulation tools is further pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in structural architecture. By leveraging these tools, we can create comprehensive, detailed architecture structure diagrams that are essential for successful project realizations.
By focusing on these pillars—identifying structural requirements, ensuring clarity and precision, and utilizing the right tools and techniques—we craft structural diagrams that are both functional and aesthetically pleasing. These diagrams not only guide the construction process but also ensure the safety, stability, and longevity of the structures we design.
The Evolution of Structural Diagrams: From Hand Drafting to Digital Modeling
The evolution of structural diagrams marks a significant advancement in how engineers and architects design buildings, influencing both the functionality and aesthetics of our built environment. As we delve into the history and progression, it’s important to understand the impact of evolving tools and methodologies on the creation and interpretation of these crucial design elements.
Traditional Drawing vs. Digital Modeling
Historically, structural diagrams and architectural drawings were meticulously hand-drafted, a time-consuming process requiring high precision and skill. Traditional drawing laid the foundational skills necessary for architectural design, emphasizing the physical relationship between different structural elements. Architects and engineers used pencils, rulers, and compasses to translate complex structural concepts onto paper, ensuring every component was accurately represented for structural integrity and aesthetic appeal. This method, while effective, was inherently limited in its ability to easily share, modify, and replicate designs.
The introduction of digital modeling transformed this process entirely. Software tools like AutoCAD and Revit have revolutionized architectural design, enabling professionals to create detailed, three-dimensional architecture structure diagrams far more efficiently than was possible with hand-drawing. Digital models facilitate a comprehensive view of a structure, allowing for immediate adjustments, enhanced collaboration among stakeholders, and a seamless integration of new data as a project evolves. This shift from traditional drawing to digital modeling has not only improved the accuracy and detail of structural diagrams but also significantly accelerated the design phase of construction projects. For a look at the essential architecture tools in 2026, explore our comprehensive overview.
The Role of BIM and AI in Modern Structural Diagrams
Building Information Modeling (BIM) has taken the structural diagram architecture workflow to a new level. Unlike traditional 2D or even 3D CAD drawings, BIM creates an intelligent, data-rich model where every structural element carries information about its material properties, load capacity, cost, and maintenance schedule. This means that an architectural diagram produced through BIM is not just a visual representation—it is a living database that can be queried, simulated, and updated throughout the building’s lifecycle.
Artificial intelligence is further enhancing the process. AI-driven tools can now analyze structural data to optimize material usage, predict potential failure points, and suggest design improvements automatically. When combined with BIM’s collaborative environment, AI enables architects and structural engineers to iterate on designs faster and with greater confidence than ever before. This convergence of technologies is redefining what it means to create a structural diagram in contemporary practice.
Structural Diagram Architecture: Best Practices for Professionals
For architects and engineers seeking to produce the most effective architectural structural diagrams, a set of best practices can make the difference between a diagram that merely documents and one that truly communicates. First, always begin with a clear hierarchy: distinguish primary load-bearing elements from secondary and non-structural components using consistent line weights and shading conventions. Second, annotate thoroughly but concisely—every dimension, material specification, and connection type should be labeled without cluttering the drawing.
Third, coordinate your structural diagrams with other disciplines early. Clash detection between structural, mechanical, and electrical systems prevents costly rework on site. Fourth, use layered digital files that allow different team members to view only the information relevant to their scope, while maintaining a single source of truth. Finally, always validate your diagrams against current local and international codes, and have them peer-reviewed before submission. These practices ensure your architecture structure diagram is not only technically sound but also a reliable communication tool across the entire project team. For further inspiration on visual communication, browse our collection of conceptual diagrams and bubble diagrams.
- architectural and structural
- architectural diagram
- Architectural Diagram Concept
- Architectural Diagram Design
- Architectural Diagram Types
- Architectural Diagrams
- architectural diagrams guide
- Architectural Programmatic Diagrams
- architecture structure diagram
- arhitecture diagram
- Circulation Diagram
- How to Create Architectural Diagram
- identify the structures on the diagram
- Programmatic Diagrams
- structural architecture
- structural diagram
- structural diagram architecture
- Structural Diagram Design
- Structural Diagrams
- structure diagram architecture
- structure diagrams
- what is a diagram in architecture
Architect/Tifa Studio Founder/Writer ▪️Sherlock Holmes, but for cities ▪️Architect | PhD | Professional outsider ▪️I see what you walk past 🔮 AI × Architecture × Unpopular opinions
1 Comment
Submit your architectural projects
Follow these steps for submission your project. Submission FormLatest Posts
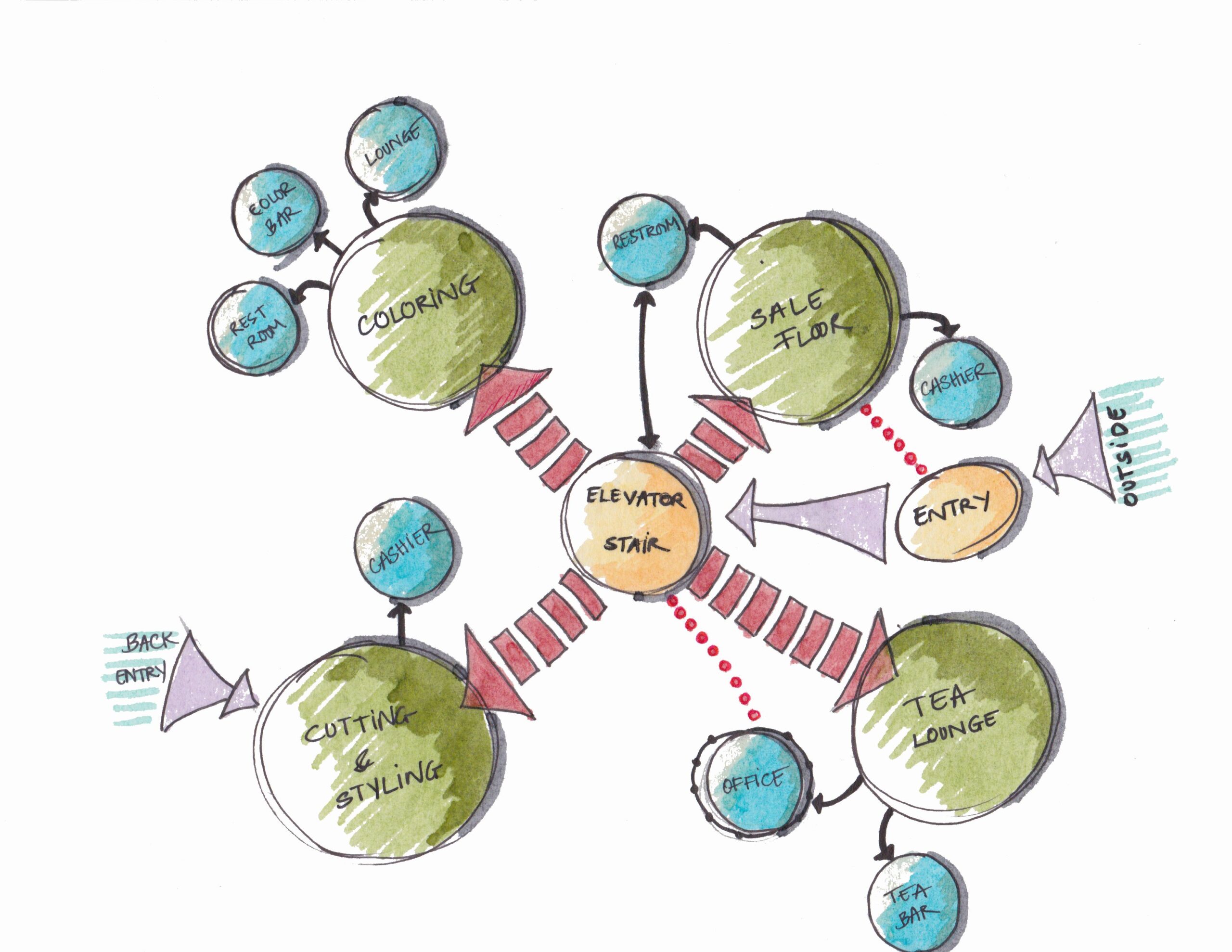
Understanding Architectural Bubble Diagrams: A Complete Guide
Architectural bubble diagrams are foundational space-planning tools that map functional relationships between...
Understanding the Role of Bubble Diagrams in Modern Architecture Design
Explore the fascinating role of bubble diagrams in modern architecture, a vital...
Architecture Circulation Diagram: Guide to Movement & Flow Design
A circulation diagram in architecture is a visual tool that maps how...
Bubble Diagram In Architecture
Bubble diagrams are essential tools in the early stages of architectural design,...









This article explains structural diagrams well. I learned a bit about how they help in construction. It seems important for buildings.